ALK (Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase) is a transmembrane molecule that is only normally expressed in some neural tissues. It has characteristic expression in a significant proportion of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALCL) cases. It has also been expressed in cases of pleomorphic liposarcoma, inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, Merkel cell carcinoma, and a small subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas.
A subset (1-5%) of non-small cell lung carcinomas (usually adenocarcinomas) have an ELM4-ALK mutation, which is often sensitive to the tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) crizotinib (Pfizer). Newer TKIs, including ceritinib (Novartis) and alectinib (Hoffmann-La Roche), have also been found to be effective.
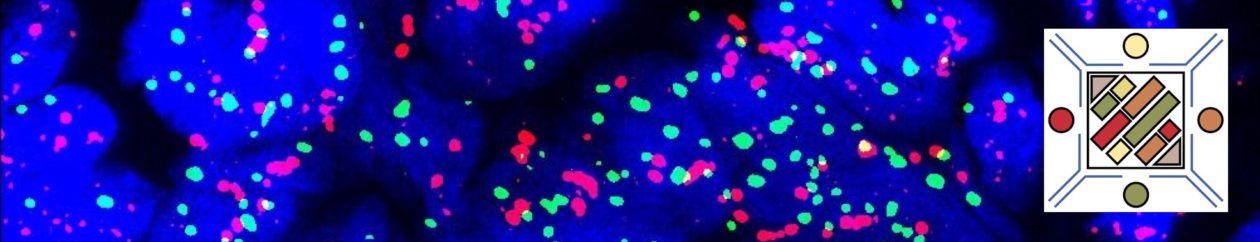
Historically, ALK translocations have been identified by FISH analysis. IHC is also an accepted method with an FDA approved test (IHC CDx Assay). PCR is being studied as an alternative. ALK antibody clones 5A4 (Novocastra, Leica Biosystems, Buffalo Grove, Illinois), ALK1 (Dako, Santa Clara, California), 1A4 (Origene, Rockville, Maryland) and D5F3 (Cell signaling Technology, Danvers, Massachusetts) have been successfully used to identify ALK mutated lung tumors, with the 5A4 & D5F3 having equivalent sensitivity.
The ALK1 clone is not as sensitive and the 1A4 clone lacks specificity compared to other antibodies. Please consult the current medical literature for FDA approved tests for ALK translocation identification in non-small cell lung carcinomas.
Normal Expression
- Neural Tissue
Abnormal Expression
- Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma
- Pleomorphic Liposarcoma
- Subset of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumors
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma (KIF5B-ALK rearrangement)
Interpretation
ALK may stain in a cytoplasmic and/or nuclear pattern. In ALCL the combined pattern of cytoplasmic and nuclear staining is associated with the t(2;5).
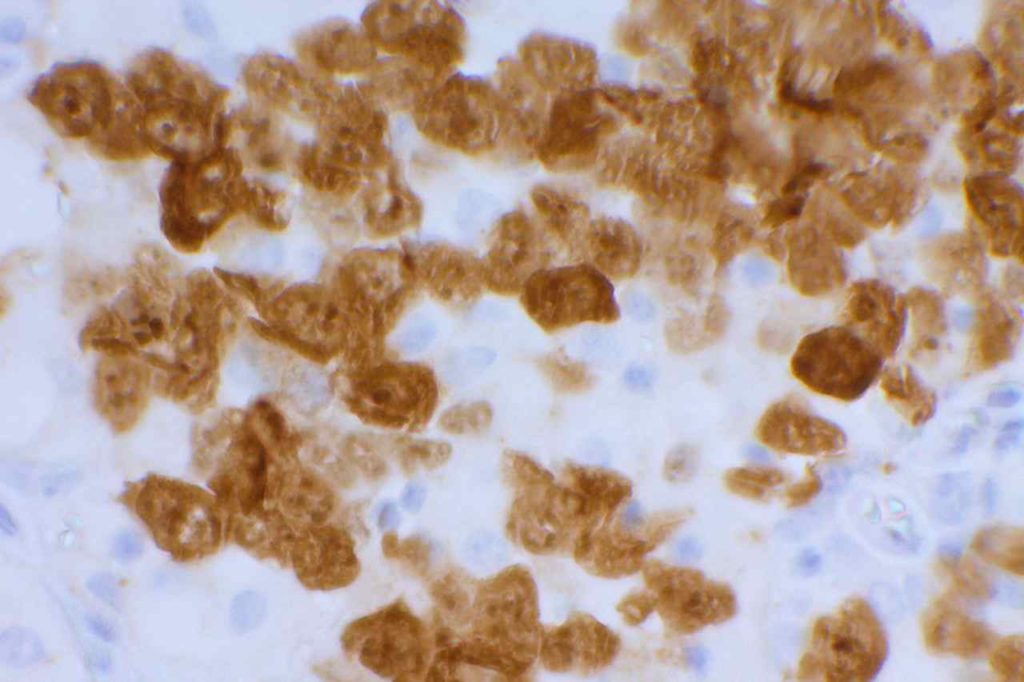
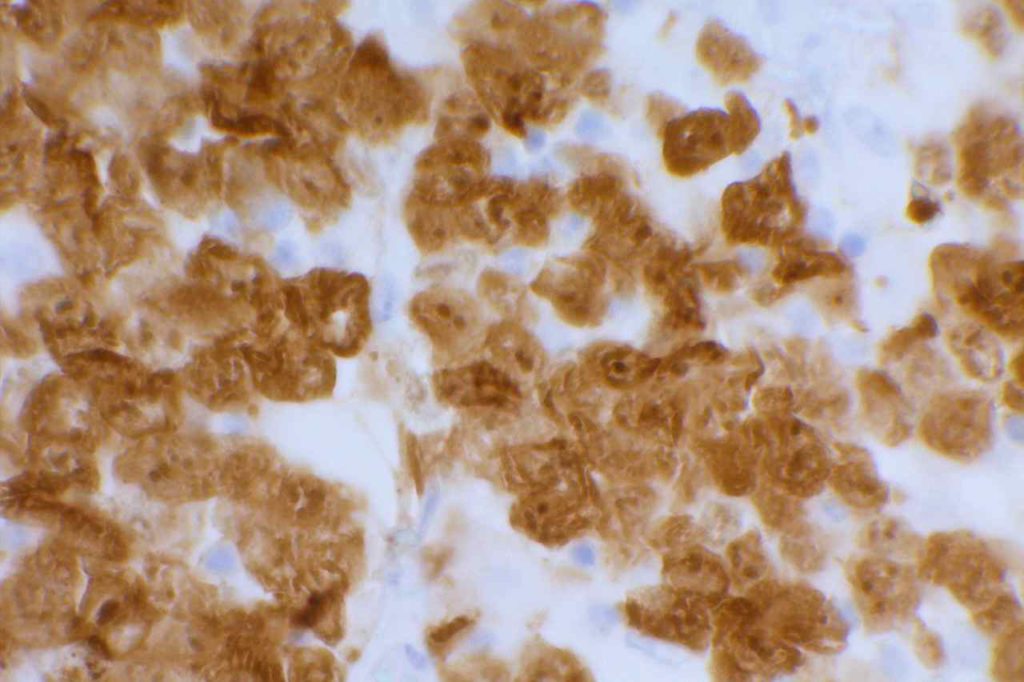
In lung ALK staining/expression is cytoplasmic. Like other markers (e.g. Napsin A), staining may be present in macrophages. Necrotic tumor, extracellular mucin, and cells of neural origin may also stain.
Photo Gallery
References
Thunnissen E, Allen TC, Adam J, Aisner DL, Beasley MB, Borczuk AC, et al. Immunohistochemistry of Pulmonary Biomarkers: A Perspective From Members of the Pulmonary Pathology Society. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142: 408–419. doi:10.5858/arpa.2017-0106-SA
Chan, J. K. C., Ip, Y. T., & Cheuk, W. (2013). The Utility of Immunohistochemistry for Providing Genetic Information on Tumors. International Journal of Surgical Pathology, 21(5), 455–475. doi:10.1177/1066896913502529
Chan, J. K. C. (2013). Newly Available Antibodies With Practical Applications in Surgical Pathology. International Journal of Surgical Pathology, 21(6), 553–572. doi:10.1177/1066896913507601
Paik, J. H., Choe, G., Kim, H., Choe, J.-Y., Lee, H. J., Lee, C.-T., et al. (2011). Screening of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Rearrangement by Immunohistochemistry in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Correlation with Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization. Journal of Thoracic Oncology : Official Publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 6(3), 466–472. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e31820b82e8
Yi, E. S., Boland, J. M., Maleszewski, J. J., Roden, A. C., Oliveira, A. M., Aubry, M.-C., et al. (2011). Correlation of IHC and FISH for ALK Gene Rearrangement in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma: IHC Score Algorithm for FISH. Journal of Thoracic Oncology : Official Publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, 6(3), 459–465. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318209edb9
Mino-Kenudson, M., Chirieac, L. R., Law, K., Hornick, J. L., Lindeman, N., Mark, E. J., et al. (2010). A novel, highly sensitive antibody allows for the routine detection of ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinomas by standard immunohistochemistry. Clinical Cancer Research : an Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, 16(5), 1561–1571. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2845
Reichard, K. K., McKenna, R. W., & Kroft, S. H. (2007). ALK-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: report of four cases and review of the literature. Modern Pathology : an Official Journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc, 20(3), 310–319. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800742
Medeiros, L. J., & Elenitoba-Johnson, K. S. J. (2007). Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. American Journal of Clinical Pathology, 127(5), 707–722.
Takeuchi K, Choi YL, Togashi Y, et al. KIF5B-ALK, a novel fusion oncokinase identified by an immunohistochemistry-based diagnostic system for ALK-positive lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(9):3143–3149. doi:10.1158/ 1078-0432.CCR-08-3248.