Renal Cell Carcinoma
The use of IHC in the setting of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) usually falls into one of two categories: (1) carcinoma of unknown primary, or (2) differentiation of RCC subtypes. Dependent upon which category one is in dictates what type of panel to utilize.
RCC vs. Other Malignancy
|
>80% expression in RCC
|
|
|
>80% expression in RCC
|
|
|
CK7/CK20
|
Both typically negative in clear cell RCC
|
|
>95% expressión in convencional clear cell RCC
|
|
|
>85% expression in clear cell and papillary subtypes
|
|
|
Variable but usually positive (author’s experience)
|
|
|
Positive
|
RCC Conventional Clear Cell type is one of a limited differential with co-expression of vimentin and cytokeratin.
RCC Subtype Differentiation
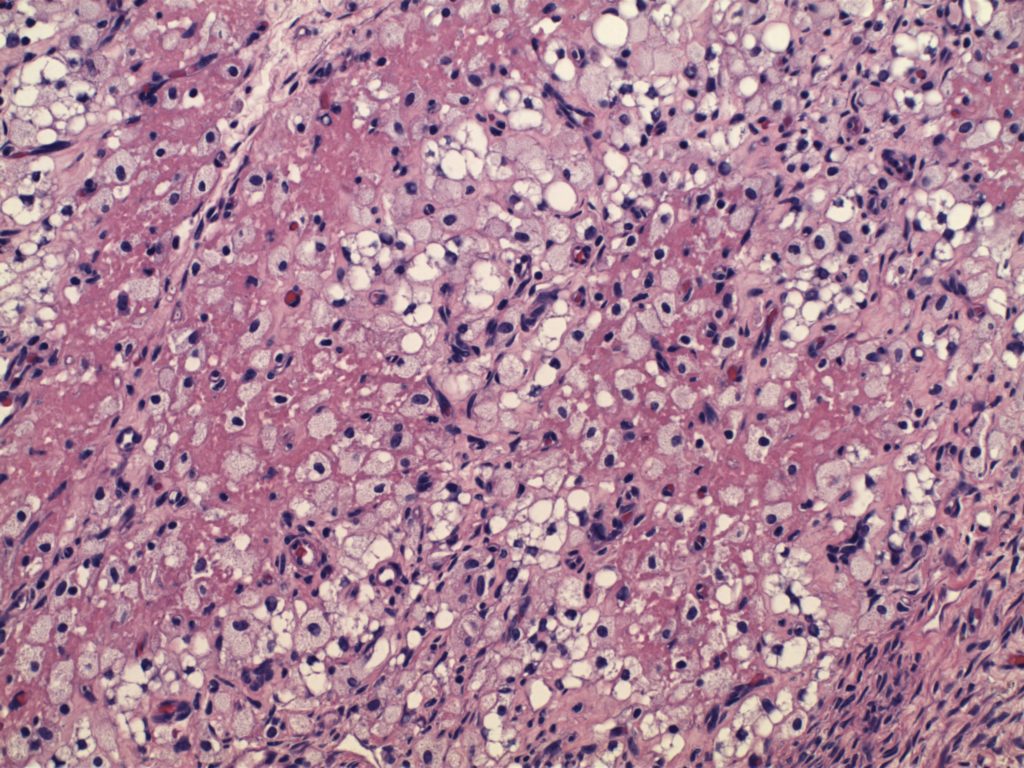
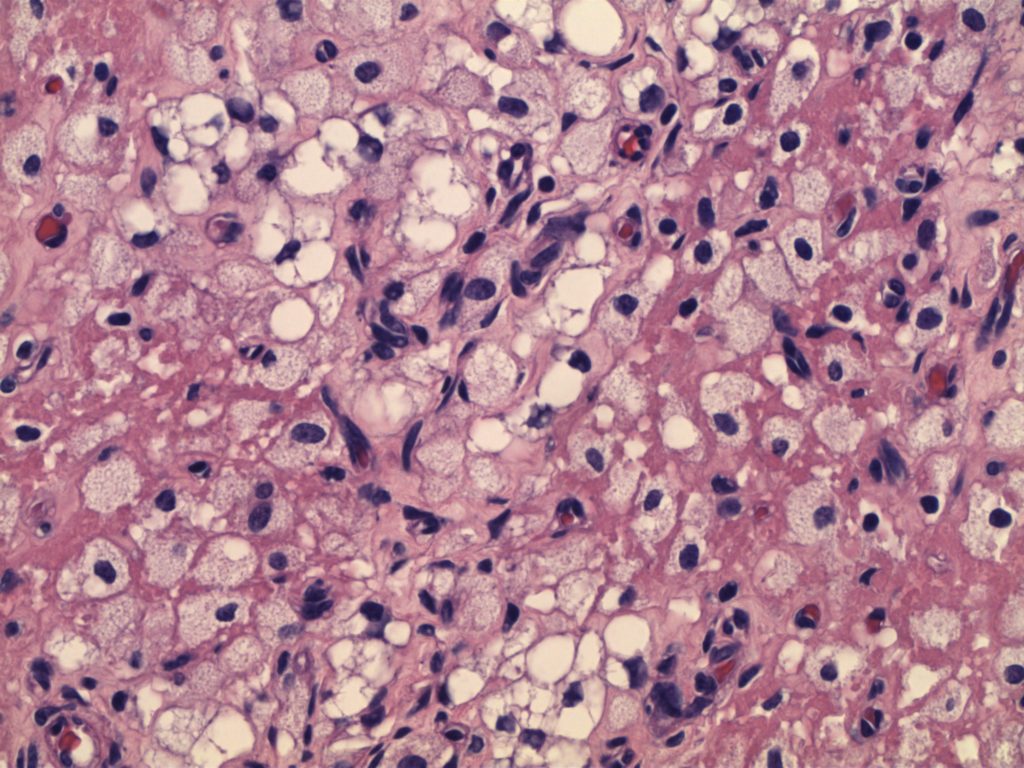
IHC may be helpful in sub-typing a RCC tumor. This usually occurs in the setting of differentiating between a chromophobe RCC and a conventional clear cell RCC with eosinophilic cytoplasm. The best way to confirm a clear cell RCC is to take more sections, and definitively identify clear cell areas. Unfortunately, on small biopsies this may not be possible, and IHC provides helpful clues.
|
Negative in chromophobe RCC/oncocytoma, and >85%+ in clear cell RCC.
|
|
|
Usually expressed in most RCCs, but literature varies widely. CAM5.2 probably better consistency and sensitivity.
|
|
|
>80% + in chromophobe RCC/oncocytoma, and negative (<5%+) in clear cell RCC.
|
|
|
Oncocytomas are usually negative for CK7, while chromophobe RCC is often positive.
|
|
|
Almost all oncocytomas and chromophobe RCCs show expression of E-Cadherin. Clear cell and papillary RCCs are typically negative. Xp11.2 translocation RCC are usually positive.
|
|
|
TFE3 is a specific marker for Xp11.2 translocation renal cell carcinomas, and is expressed in >90% of such cases.
|
As a general rule of practice in IHC, it is best to have both positive and negative markers for differentiation.
|
IHC Stain
|
RCC
Clear Cell
|
RCC
Papillary
|
RCC
Chomophobe
|
RCC
Xp11.2
|
|
94-100%
|
67-93%
|
+/- 0-72%
|
+ >90%
|
|
|
0-37%
|
80-87%
|
73-86%
|
17%
|
|
|
=
|
=
|
=
|
N/A
|
|
|
35% (varies)
|
82%
|
16%
|
11%
|
|
|
87%
|
100%
|
=
|
66%
|
|
|
92%
|
87%
|
+/- 0-82%
|
|
|
|
98%
|
87%
|
83%
|
|
|
|
72-85%
|
87-95%
|
0-91%
|
|
|
|
0-5%
|
0-13%
|
82-100%
|
|
|
|
88%
|
>90%
|
>90%
|
|
|
|
Negative
|
Negative
|
Positive
|
68%
|
AE1/AE3 has varying positivity in the literature. Part of this is probably due to that AE1/AE3 lacks CK18, which is expressed by most RCCs. Other CKs have varying expression. CAM5.2 is recommended over AE1/AE3.
Differential Diagnosis
Adrenocortical Carcinoma: AE1/AE3 -, EMA -, RCC Ma., Inhibit +, Calretinin +
Angiomyolipoma: MART-1 +, HMB-45 +, Tyrosinase +, Smooth Muscle Markers +, Cytokeratins -, EMA –
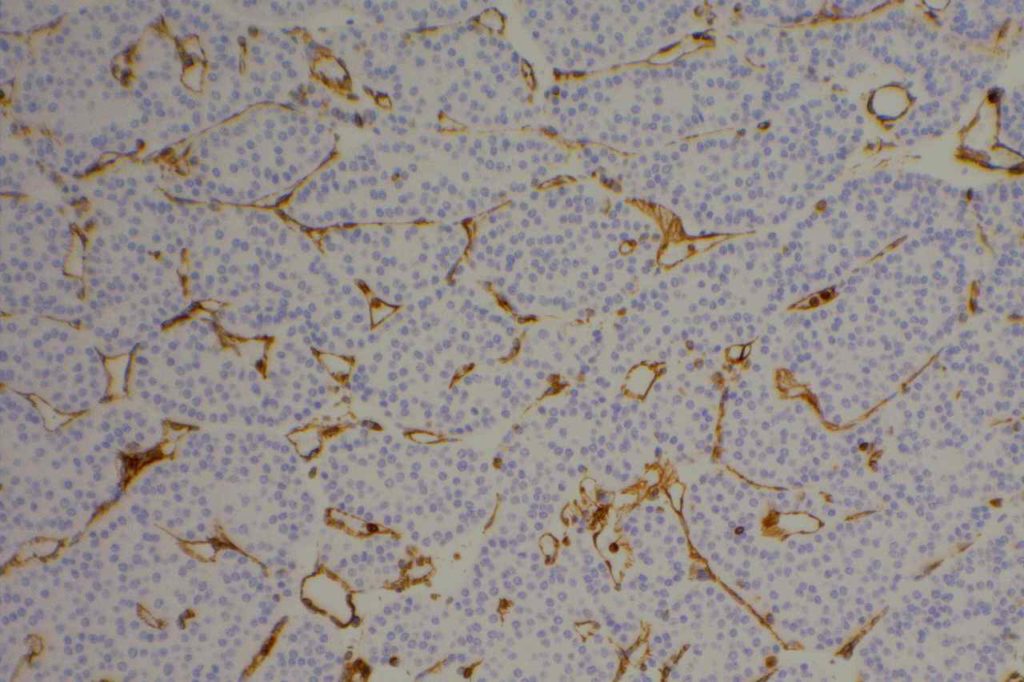
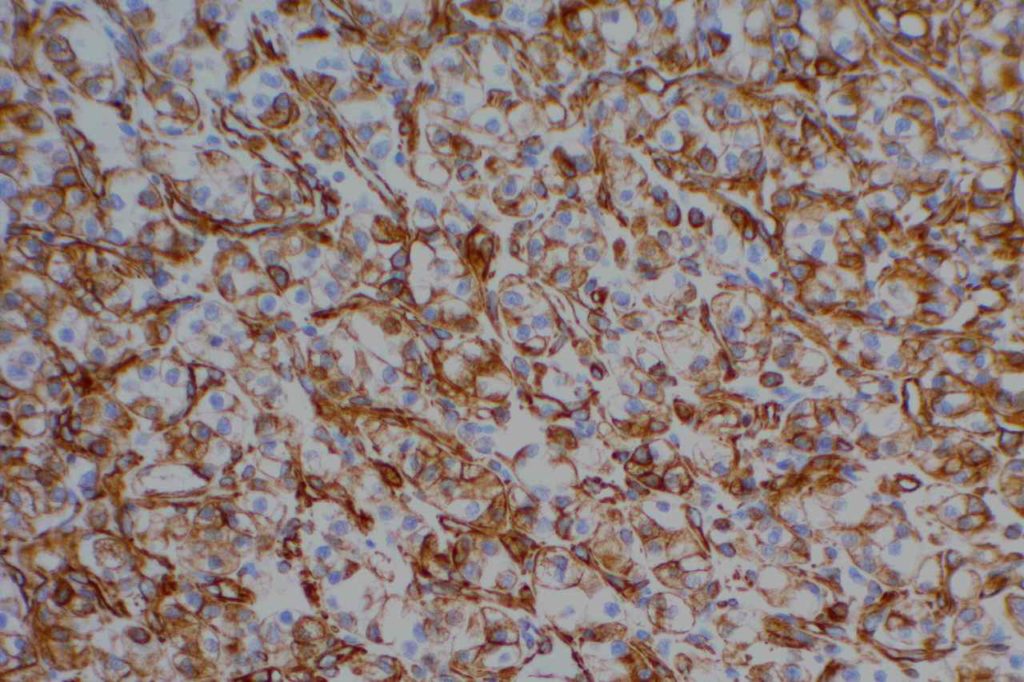
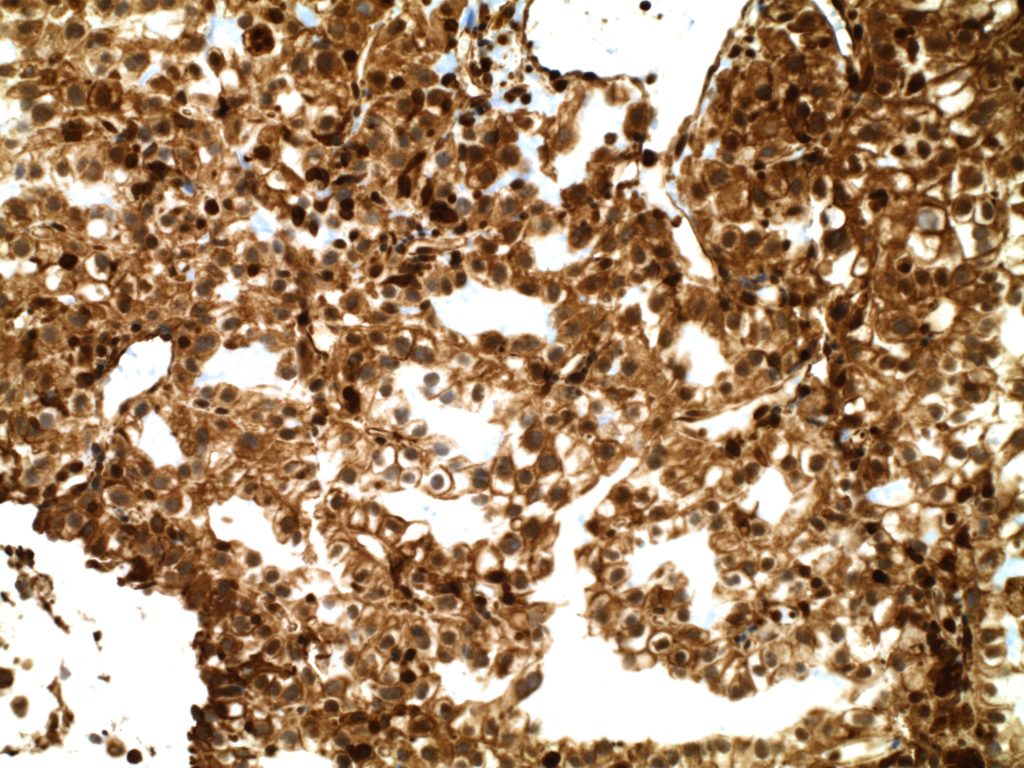
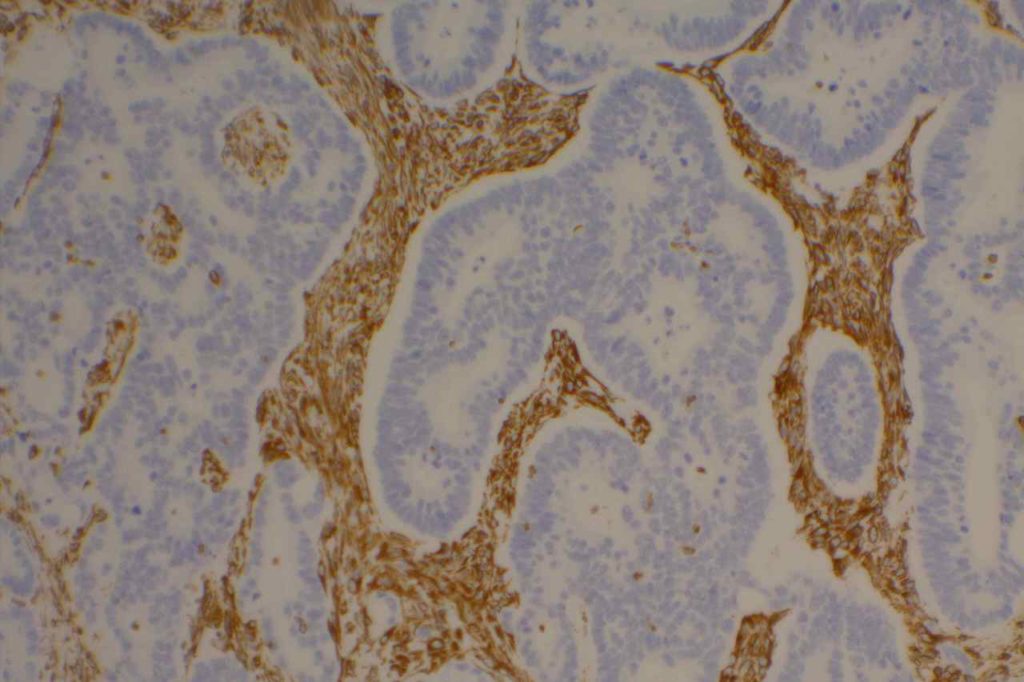
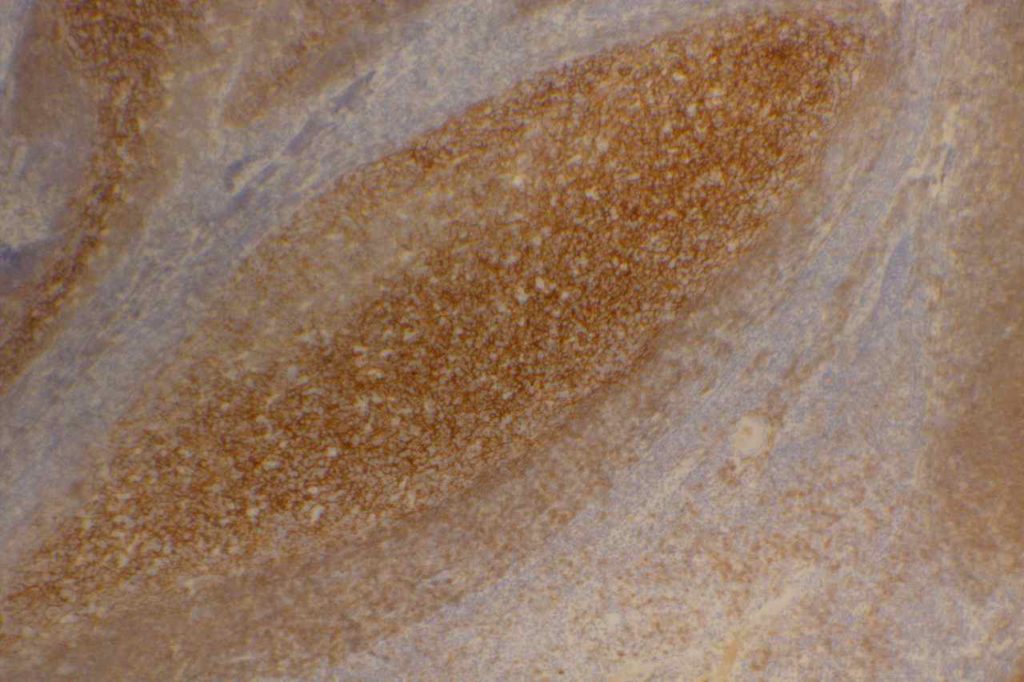
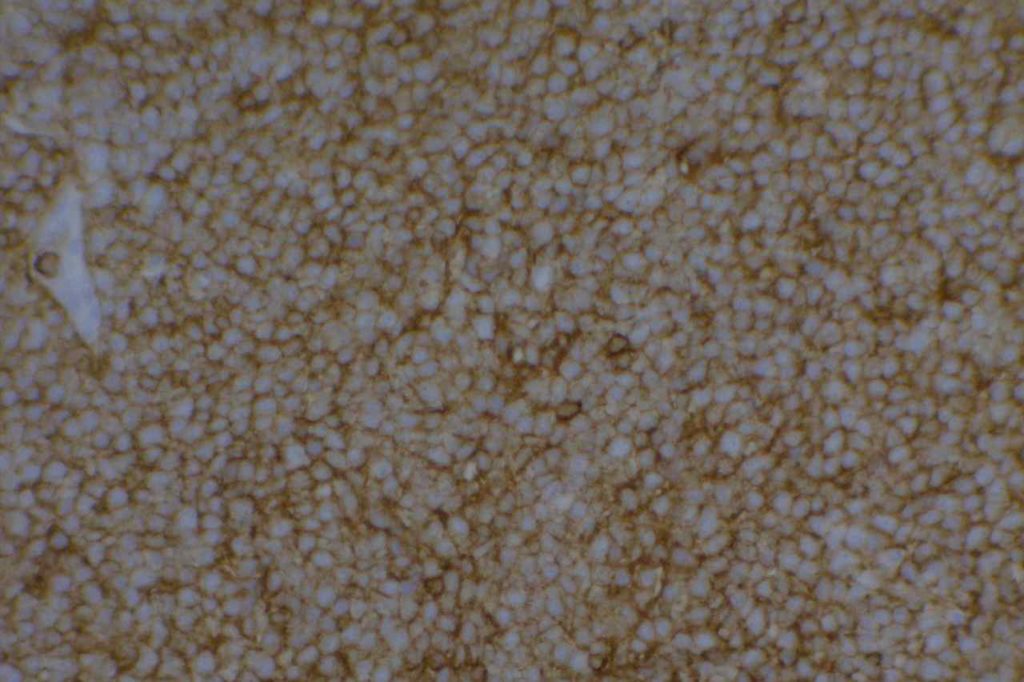
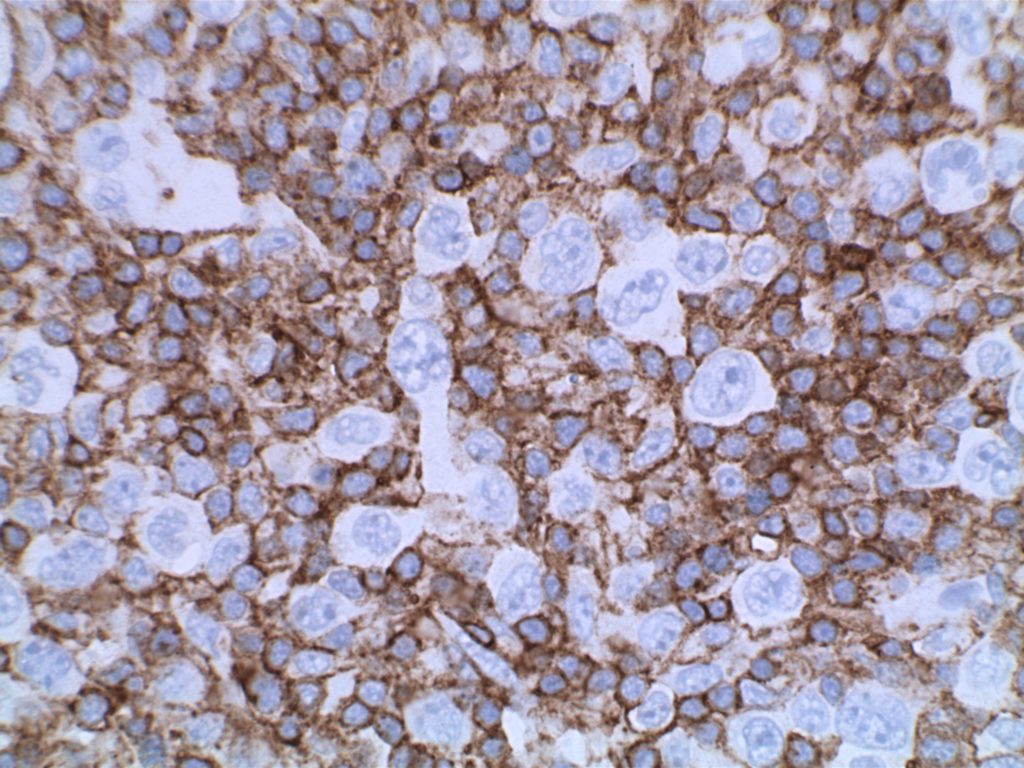
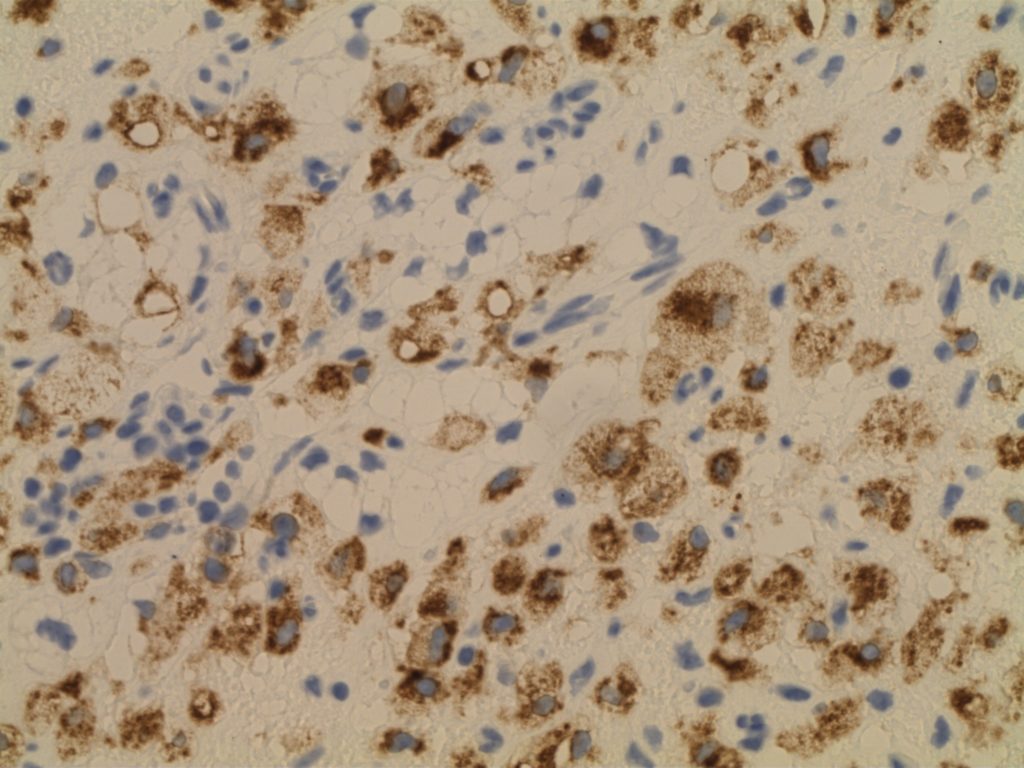
Photomicrographs



References
Arch Path Lab Med – Vol. 135, Jan. 2011 (Truong & Shen).
Pan, CC. “Differential Immunoprofiles of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Renal Cell Carcinoma, and Adrenalcortical Carcinoma.” Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. Vol. 13, No. 4, Dec. 2005.
Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry: Theranostic and Genomic Applications. [edited by] DJ Dabbs. 3rd Edition. Elsevier, 2010.
Shen, SS. “Role of Immunohistochemistry in Diagnosing Renal Neoplams: When Is It Really Useful?”Arch Pathol Lab Med, Vol. 136, April 2012. pp. 410-417.
Camparo, P., Vasiliu, V., Molinie, V., Couturier, J., Dykema, K. J., Petillo, D., et al. (2008). Renal translocation carcinomas: clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and gene expression profiling analysis of 31 cases with a review of the literature. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 32(5), 656–670. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181609914