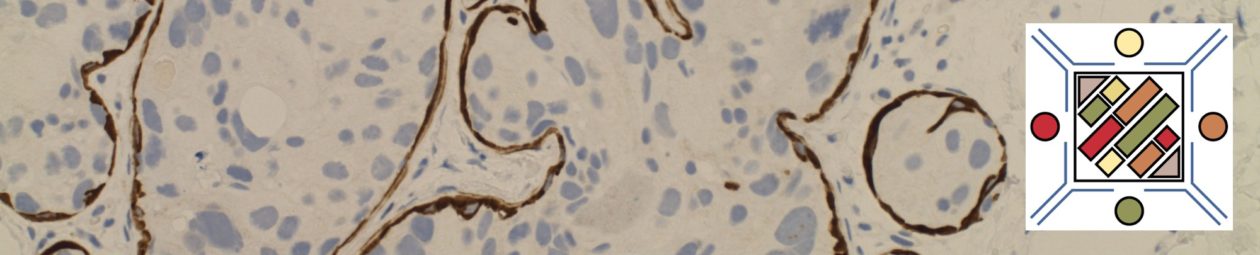
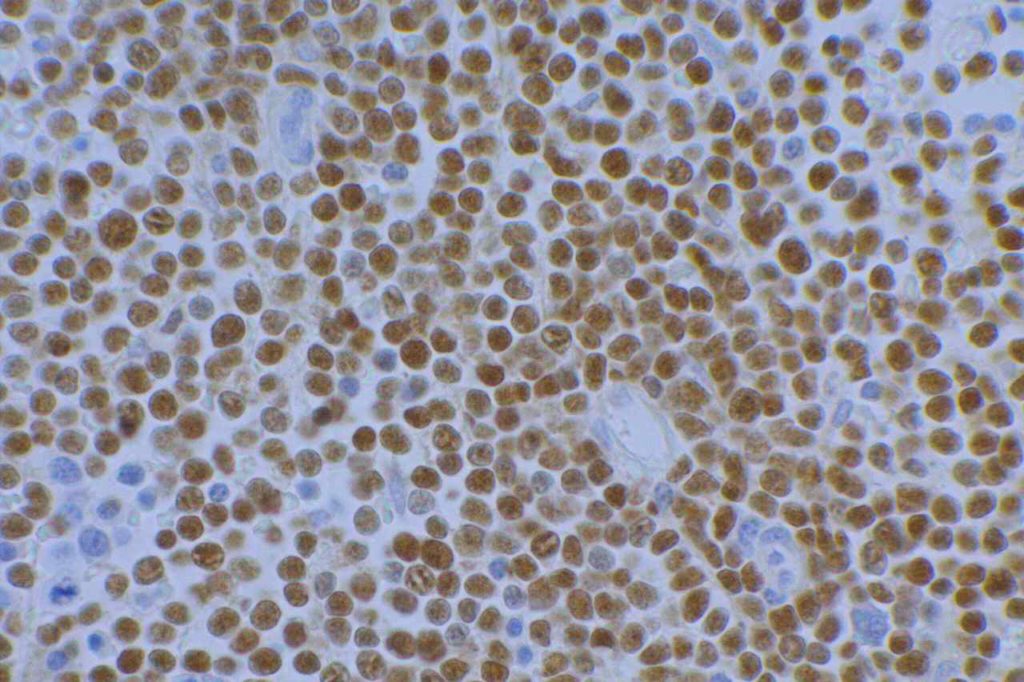
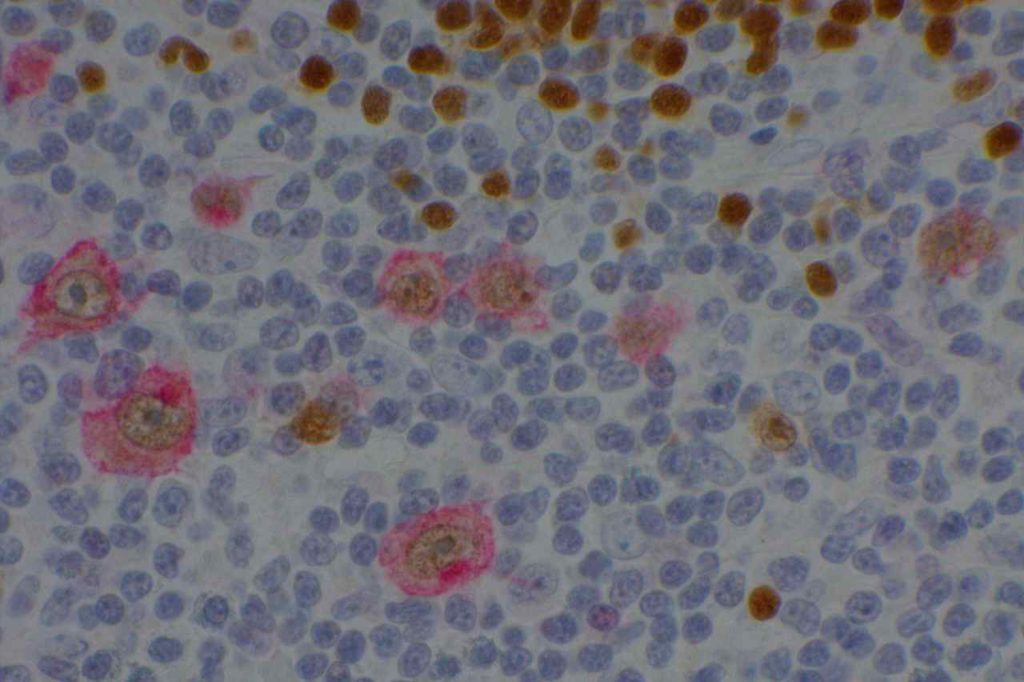
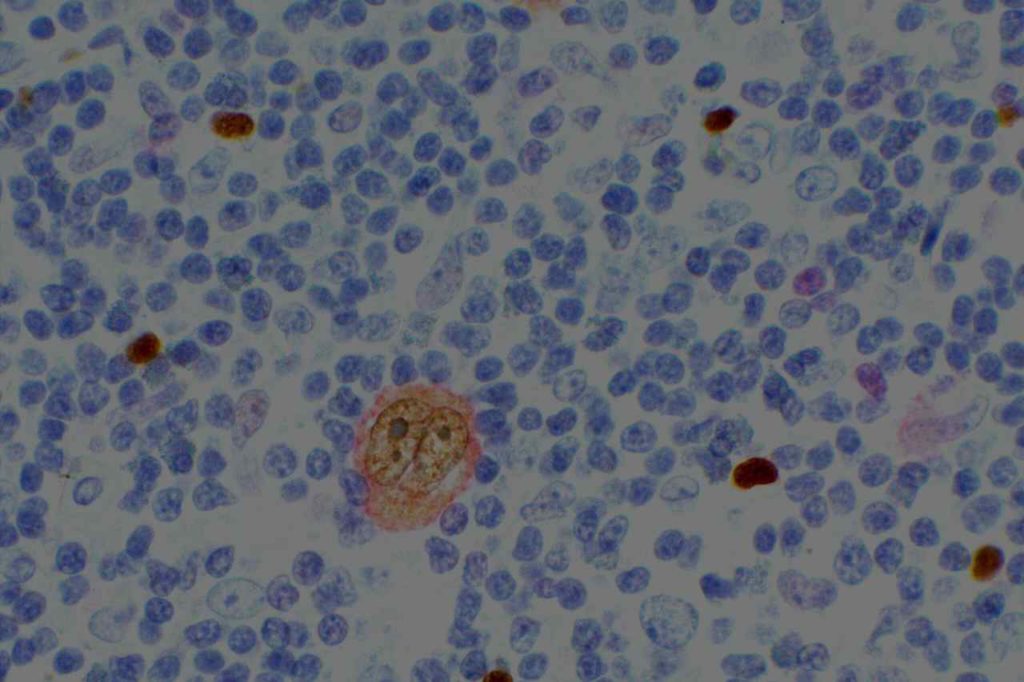
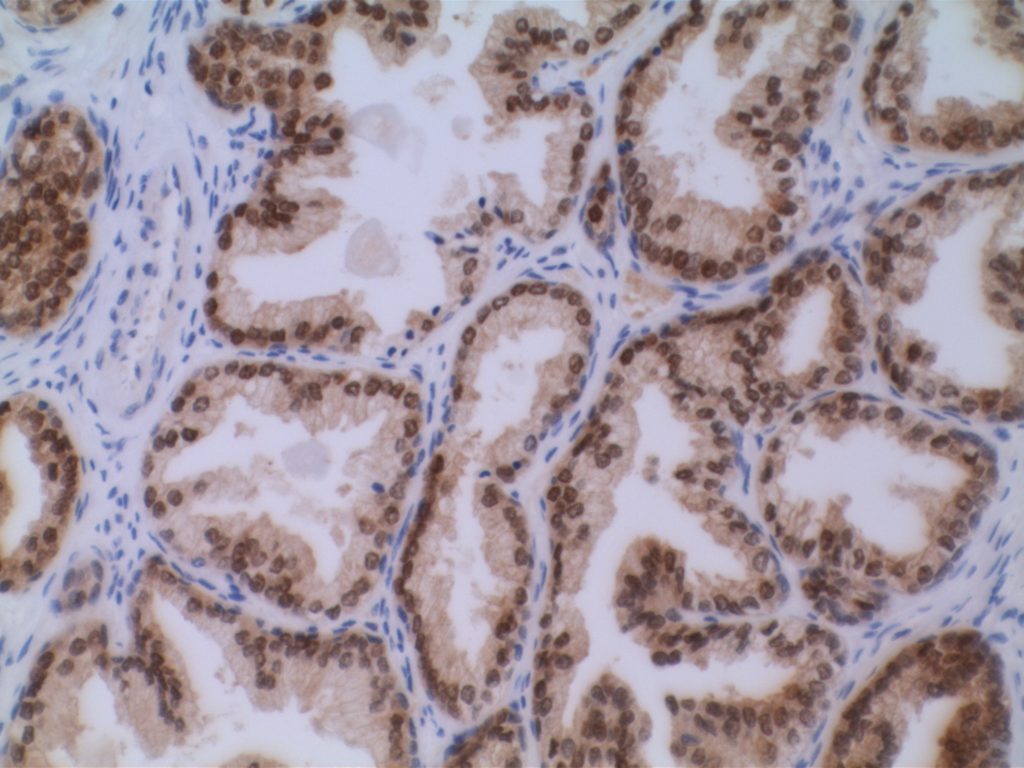
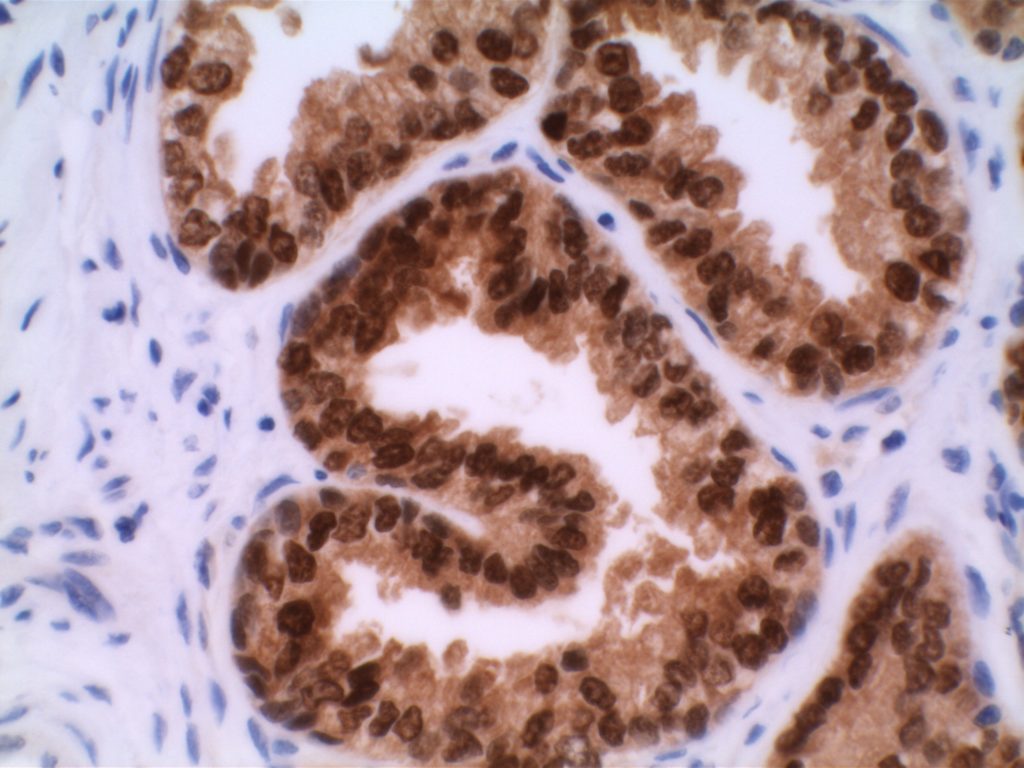
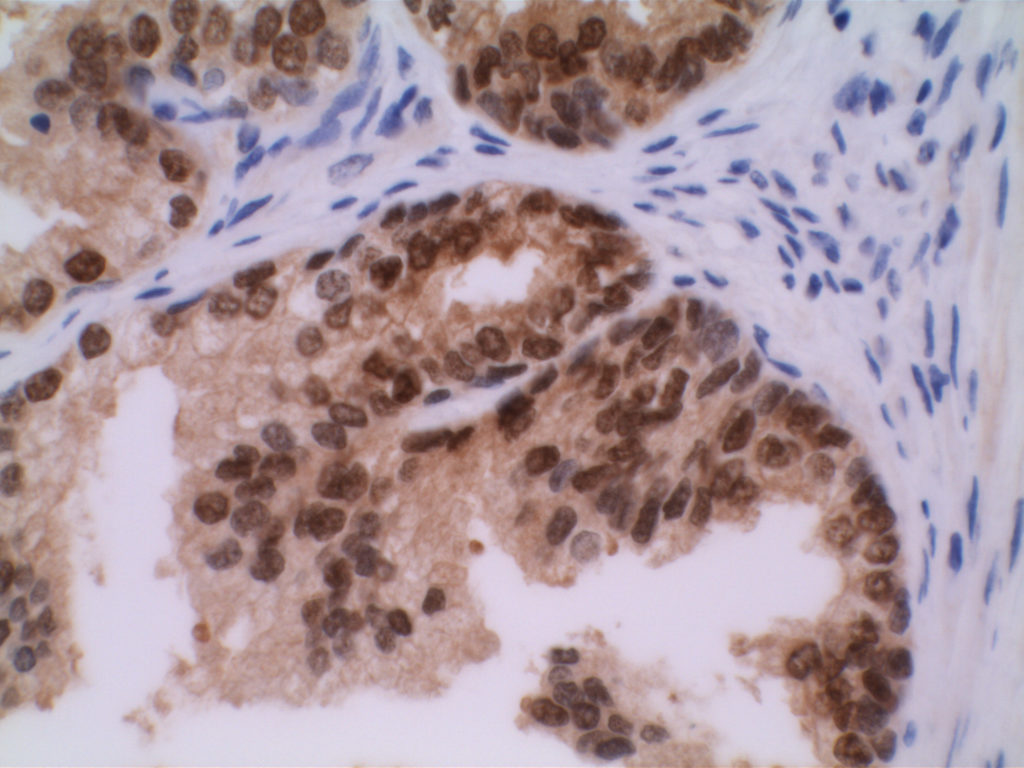
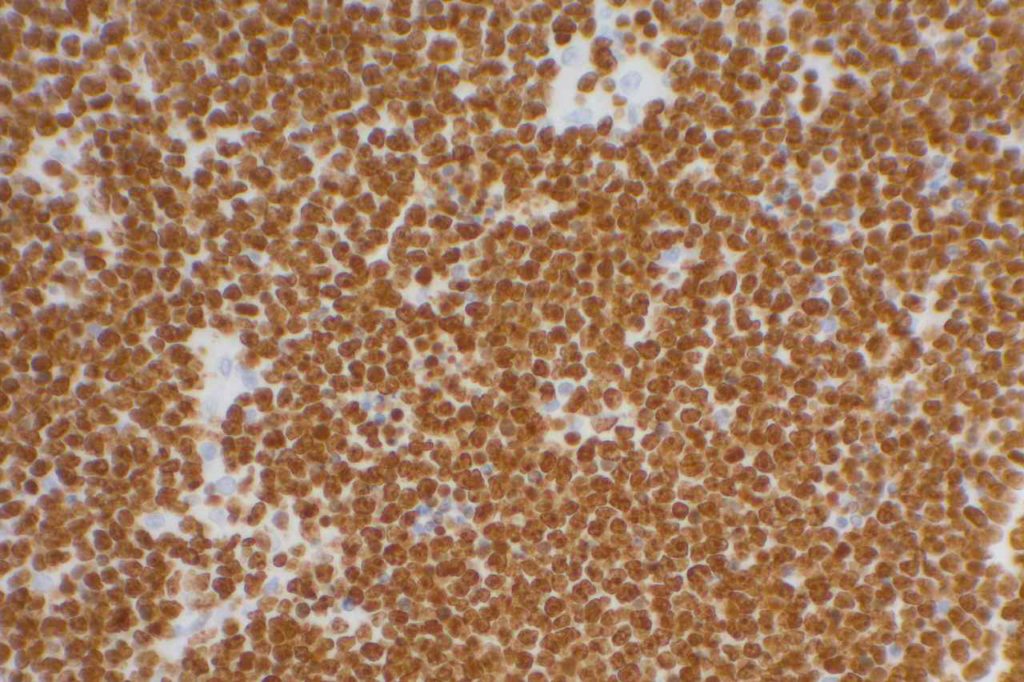
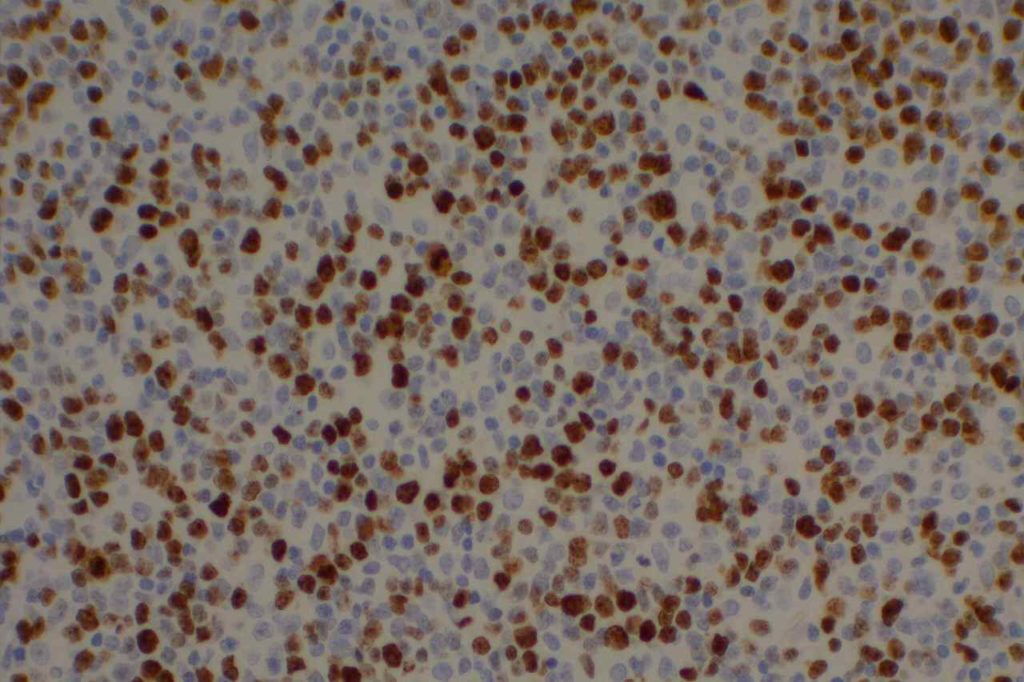
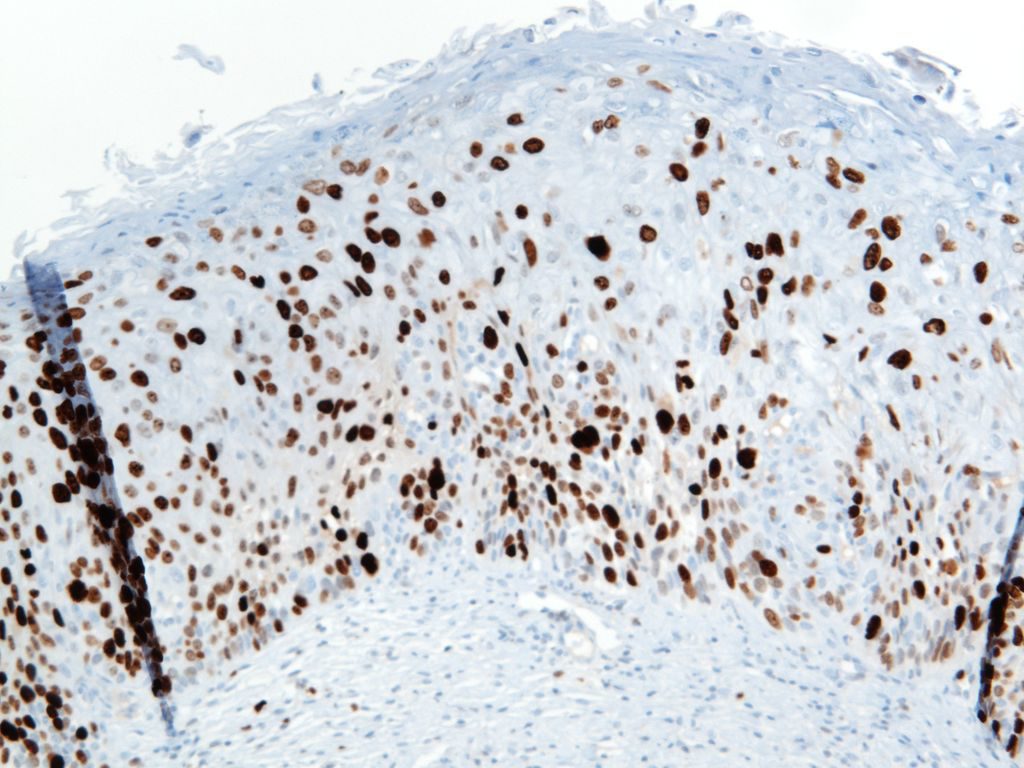
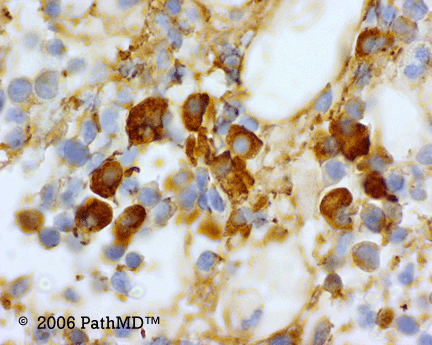
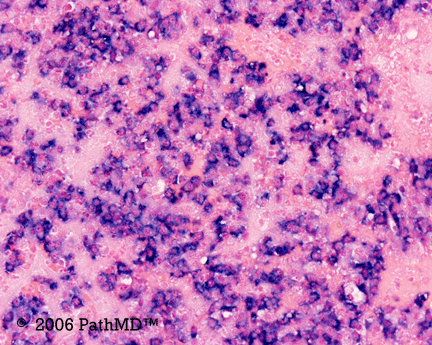
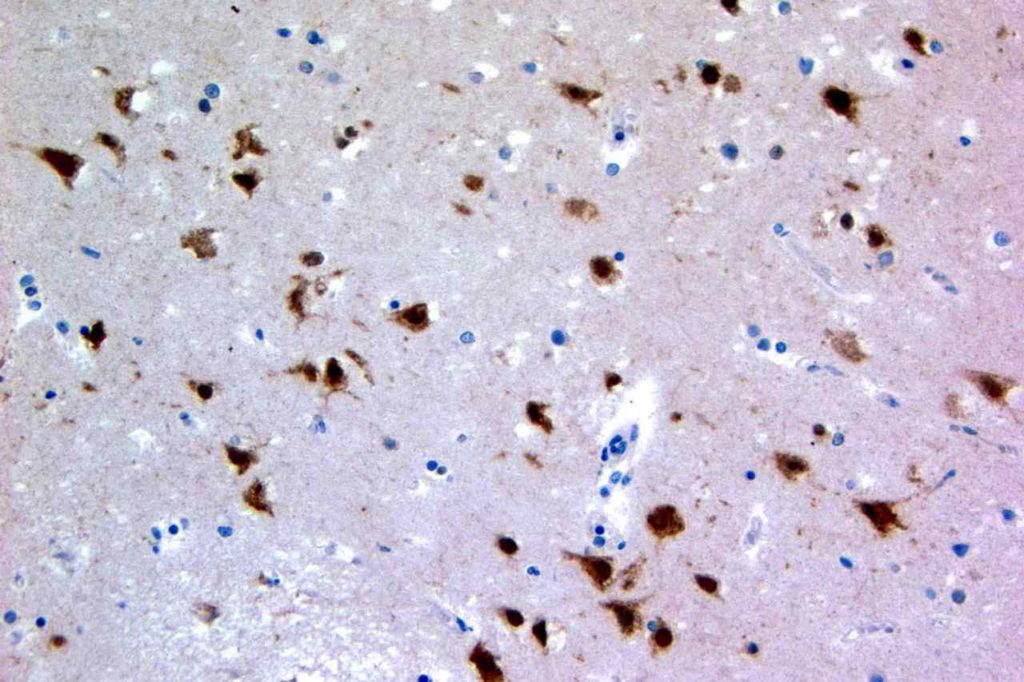
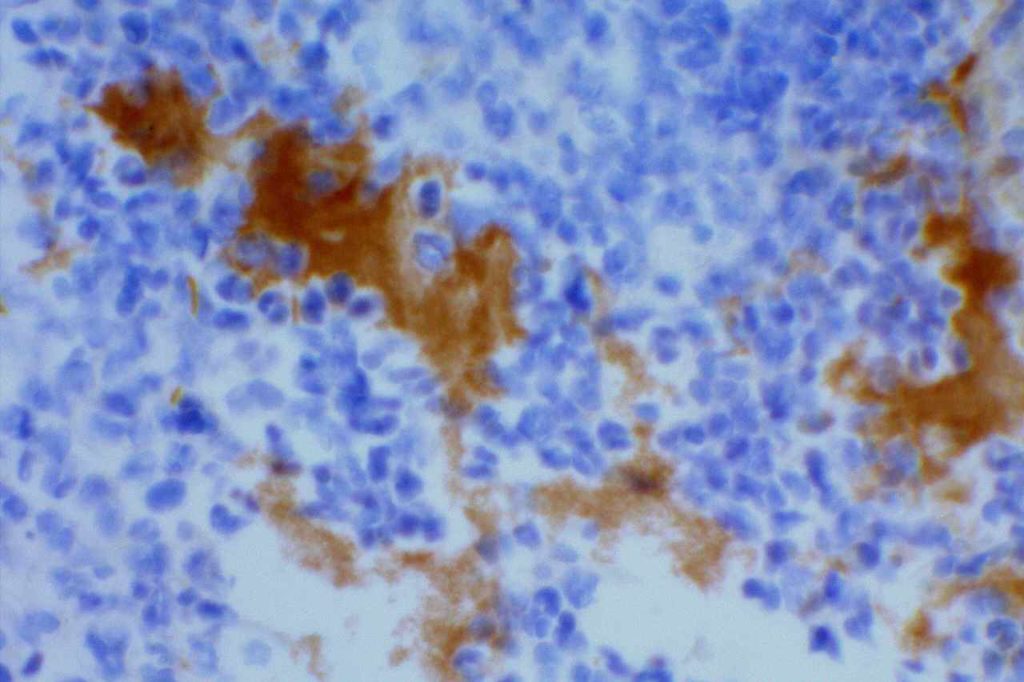
p40 is a member of the p53 family, and is an isoform of p63. It is also known as delta-Np63. p63 can have different isoforms, and p40 reacts with truncated dominant isoforms of the p63 gene. (Brown, et. al.; Bishop, et. al.; and Ross, et. al.) p40 performs in a similar fashion to p63, but with so-called better specificity. (Bishop)
p40 appears very sensitive for lung squamous cell carcinomas (>90%) and urothelial carcinomas (>88%) from multiple studies. (Gaily, et. al. and Bishop, et. al.) Rarely (<5%) breast, biliary tract/pancreas, endometrium, and prostate showed reactivity, and evaluation of multiple cases (40-100 each) of renal cell carcinoma, thyroid, hempatocellular carcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, stomach adenocarcinoma, and ovarian epithelium failed to show any reactivity (negative). (Brown, et. al.)
General Comments
Ross, et. al. claims superiority of p40 over p63 because only 3% of lung adenocarcinomas showed any positivity with p40 compared to 31% with p63. To the inexperienced pathologist using p63 in lung cancer subcategorization, partial positivity with p63 may lead to comments like “focal squamous differentiation” or “cannot exclude a component of squamous cell carcinoma”. These comments should be avoided, if possible. Often oncologists will not give the patient Avastin, which is an important therapy option, if there is any evidence of squamous differentiation due to the risk of pulmonary hemorrhage.
Where some pathologists find variable subset nuclear expression with p63 in lung adenocarcinomas, others find such expression pattern as re-inforcing support for the diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma. It is important to remember a basic tenant (general rule) in interpreting nuclear transcription markers like p40 and p63; expression should be consistent and diffuse for the tumor cells of interest. If expression does not meet this threshold, then one may be wise to consider additional markers in a panel to confirm differentiation. Pathologists must NOT think of stains as positive and negative, but in the context of the pattern of expression, and what that means.
References:
Brown AF, Sirohi D, Fukuoka J, Cagle PT, Policarpio-Nicolas M, et al. (2013) Tissue-preserving antibody cocktails to differentiate primary squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and small cell carcinoma of lung. Arch Pathol Lab Med 137: 1274–1281. doi:10.5858/arpa.2012-0635-OA.
Bishop JA, Teruya-Feldstein J, Westra WH, Pelosi G, Travis WD, et al. (2012) p40 (ΔNp63) is superior to p63 for the diagnosis of pulmonary squamous cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol 25: 405–415. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.173.
Rossi G, Pelosi G, Barbareschi M, Graziano P, Cavazza A, et al. (2013) Subtyping Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Relevant Issues and Operative Recommendations for the Best Pathology Practice. International Journal of Surgical Pathology 21: 326–336. doi:10.1177/1066896913489346.
Gailey MP, Bellizzi AM (2013) Immunohistochemistry for the novel markers glypican 3, PAX8, and p40 (ΔNp63) in squamous cell and urothelial carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 140: 872–880. doi:10.1309/AJCP4NSKW5TLGTDS.