BerEP4 is expressed on the surface and cytoplasm of epithelial cells. It does not mark superficial layers of squamous epithelium, mesothelial cells, or hepatocytes. It does mark basal layers of squamous epithelium. BerEP4 is an antibody to cell membrane glycoproteins (not cytokeratins).
BerEP4 is most often used as an adenocarcinoma marker for adenocarcinoma (80-100%) in the differential with mesothelioma (0-18%). [100% sensitive, 91% specific. AJSP 2001;25:43] As is the case in examining multiple sources in the medical literature, one must have a clear understanding of how “positive” is defined. A general take home point is that most adenocarcinomas show strong/diffuse expression compared to more dim/focal expression when found (rare) in mesotheliomas. BerEP4 is a valuable tool to help differentiate adenocarcinomas from mesothelioma, and is best used as part of a larger panel chosen for the specific differential diagnosis at hand.
Summary of multiple studies describing BerEP4 expression in various tumors (Ordones, NG)
|
Tumor
|
No.
|
Expression
(%)
|
|
Mesothelioma
|
14
|
0%
|
|
“Various Carcinomas”
|
144
|
99%
|
|
Adenocarcinoma of “various” origin
|
120
|
86%
|
|
Mesothelioma
|
49
|
20%
|
|
Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
|
35-50%
|
Skin
Basal cell carcinomas have been found to express BerEP4, compared to squamous cell carcinomas, which do not express BerEP4. Bcl-2 also has a similar expression pattern, like BerEP4, in basal cell carcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas.
General Points
- Expressed in most adenocarcinoma
- Not sensitive for renal cell carcinoma
- Dim or focal expression should be interpreted with caution
- Most adenocarcinomas show strong diffuse expression
- Use as part of a panel to differentiate mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma
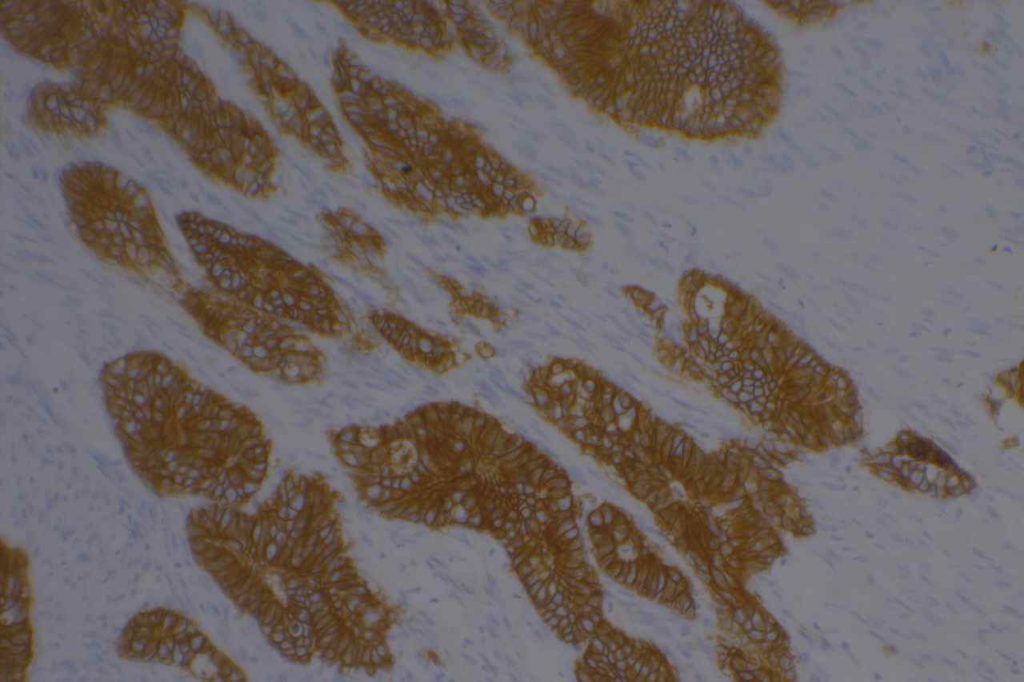
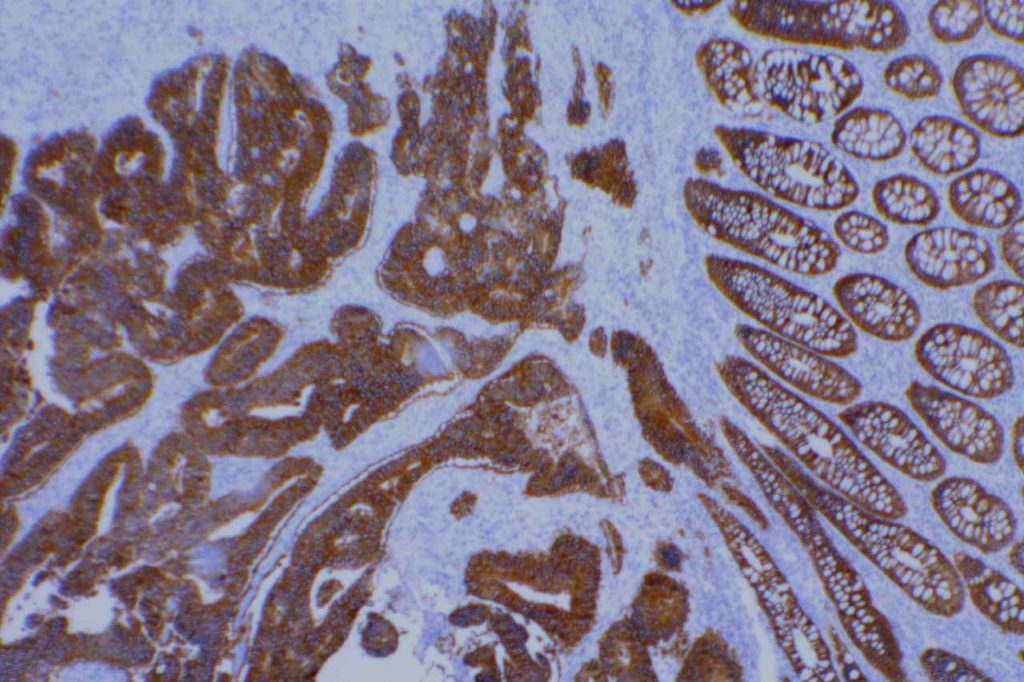
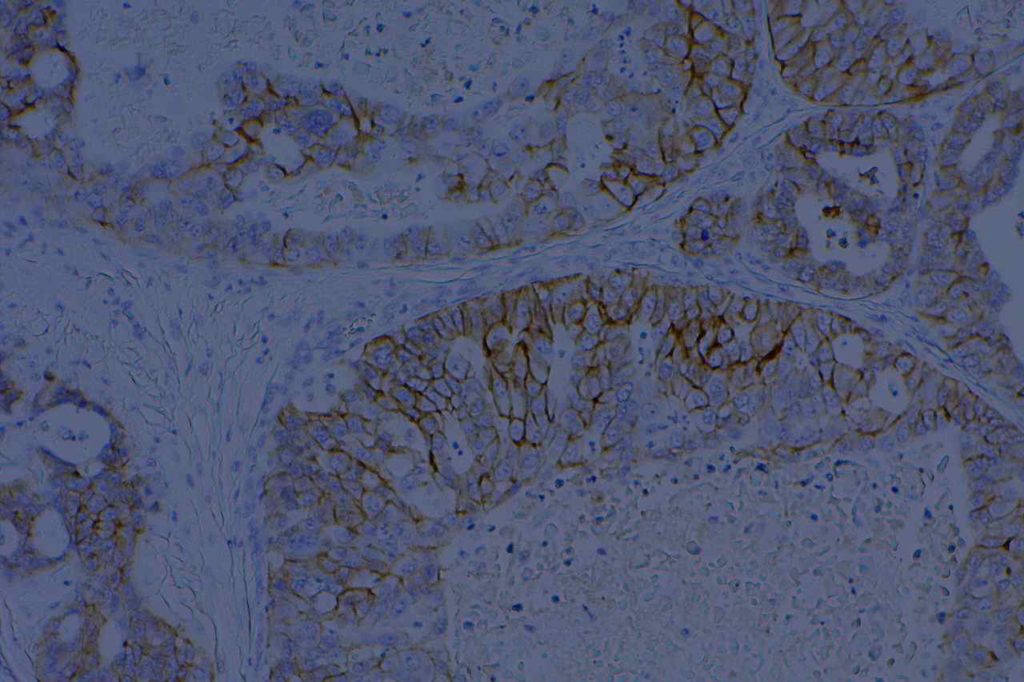
Photomicrographs
References
Ordóñez, N. G. (2005). Immunohistochemical diagnosis of epithelioid mesothelioma: an update. Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine, 129(11), 1407–1414.
Tellechea, O., Reis, J.P., Domingues, J.C., Baptista, A.P. (1993). Monoclonal antibody Ber EP4 distinguishes basal-cell carcinoma from squamous-cell carcinoma of the skin. American Journal of Dermatopathology. Oct;15(5):452-5.
Marchevsky AM. Application of immunohistochemistry to the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2008;132: 397–401.
Allende D, Yerian L. Immunohistochemical Markers in the Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pathology Case Reviews. Vol. 14: 40–46.
Sandeck HP, Røe OD, Kjærheim K, Willén H, Larsson E. Re-evaluation of histological diagnoses of malignant mesothelioma by immunohistochemistry. Diagnostic pathology. 2010;5: 47. doi:10.1186/1746-1596-5-47