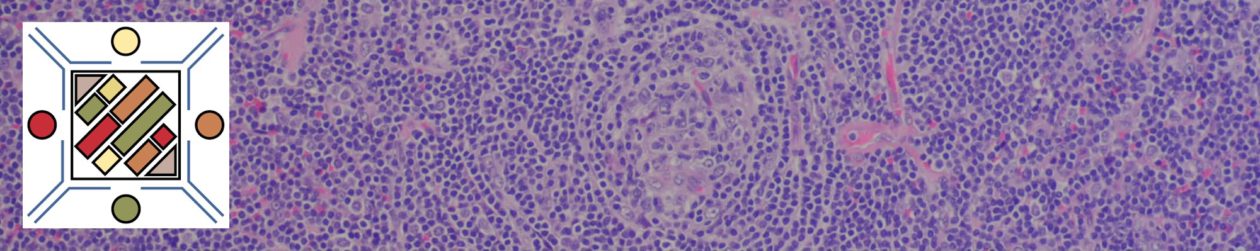
Small cell carcinoma (poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma) of the bladder is uncommon, but well documented. Small cell carcinoma can essentially occur at any site.
Most of the time neuroendocrine differentiation can be identified by immunohistochemistry. Occasionally lesions can be so poorly differentiated that it is difficult to identify neuroendocrine or even cytokeratin expression.
There are no known location specific markers for small cell carcinomas. Many (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary small cell carcinomas) express TTF-1. TTF-1 outside the setting of adenocarcinoma should not be used to support primary lung origin.
Photomicrogrpahs