Burkitt lymphoma is a high grade B cell lymphoma composed of medium-sized monomorphic lymphoid cells. The cytology of the nuclei includes finely dispersed chromatin. By touch prep, the cells resemble lymphoblasts, often with cytoplasmic lipid filled vacuoles. In tissue section, the nuclear appearance can be variable from regular round appearance to that with more irregularity.
Burkitt lymphomas are characterized by the translocation of the MYC gene usually with IGH, t(8;14)(q24;q32). Less common translocations include t(2;8) and t(8;22). Interestingly, ~10% of cases with a classic appearance and phenotype do not have an identifiable MYC rearrangement.
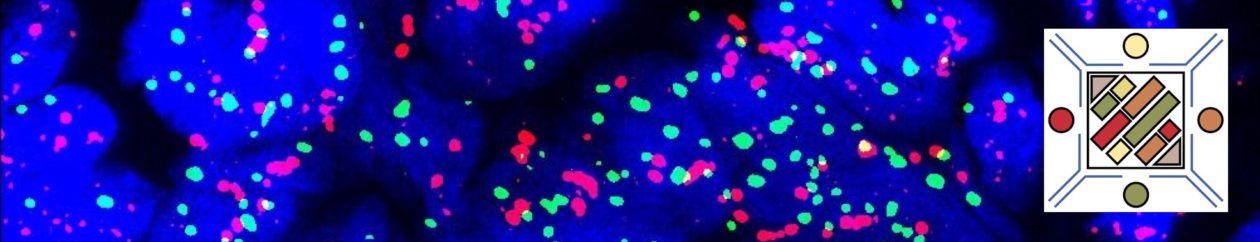
Practically, using a break apart FISH probe for the MYC gene is a simple yet efficient way of confirming the diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma.
Photomircrographs






Immunohistochemical Expression Profile
|
Negative
|
|
|
Negative
|
|
|
Positive
|
|
|
Positive
|
|
|
Positive
|
|
|
Negative
|
|
|
Negative
|
|
|
Negative
|
|
|
Positive
|
|
|
Positive
|
|
|
Negative
|
|
|
Almost 100%
|
|
|
Negative
|
|
|
p53
|
Positive
|