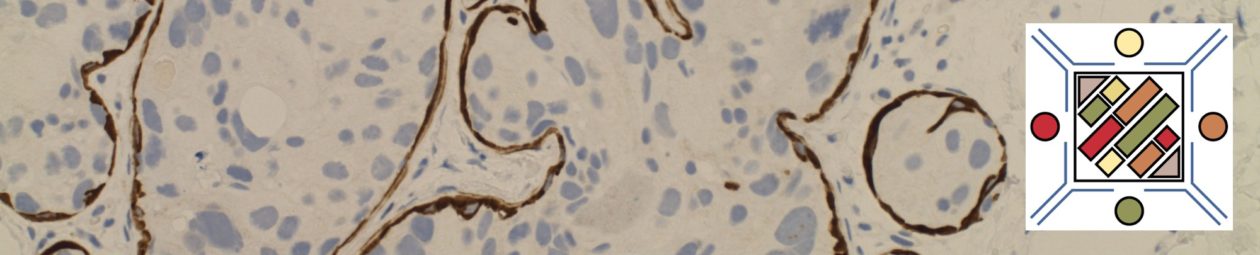
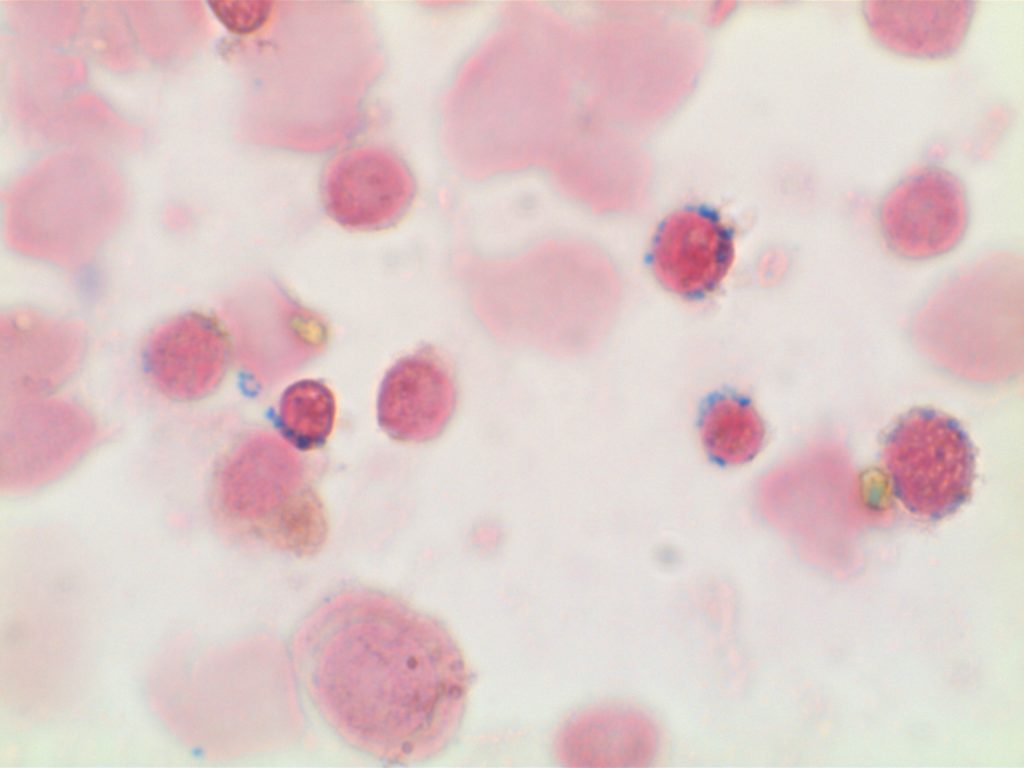
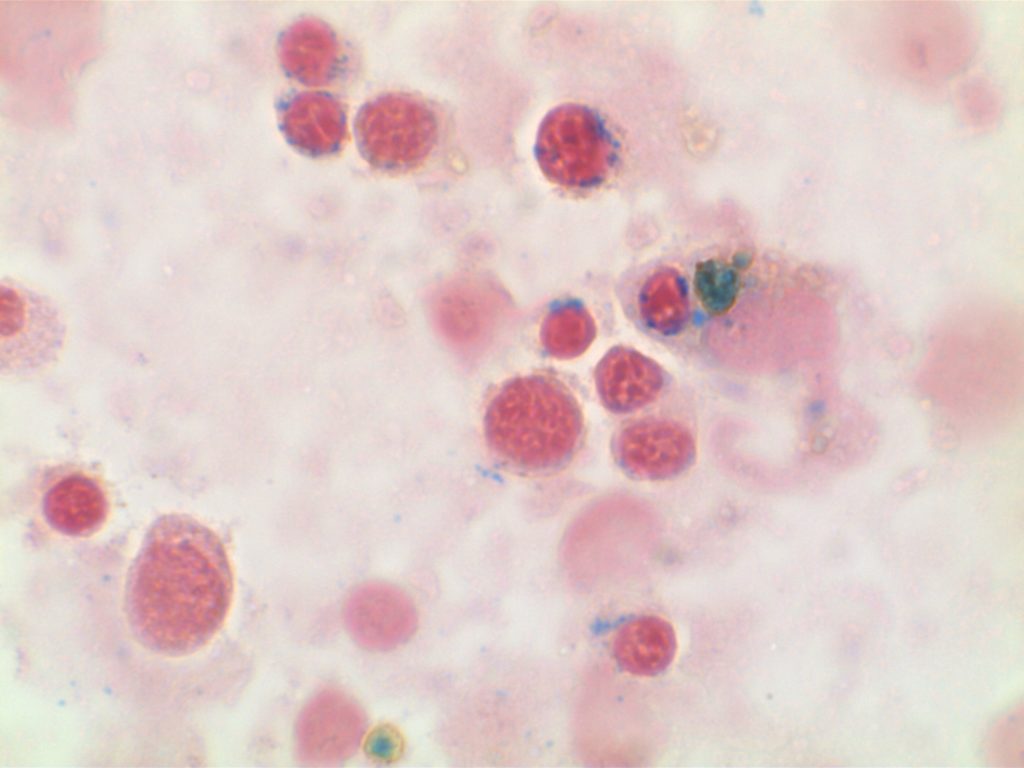
WHO Criteria for Cytopenias
- Platelet count <100,000/μL
- Hemoglobin <10g/dL
- Absolute neutrophil count <1,800/μL
The WHO Classification does state patients with MDS may present having mild cytopenias with values above the defined levels. Continue reading Cytopenia Definition