Breast lesions and risk of developing an invasive carcinoma
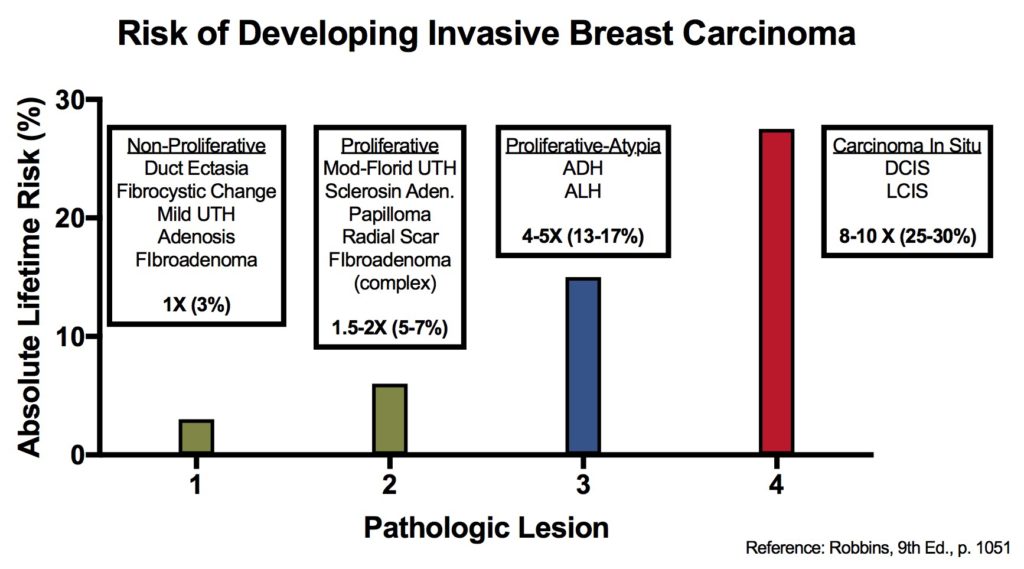
References
Kumar, Vinay, Abul K. Abbas, and Jon C. Aster. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Ninth edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2015.

Kumar, Vinay, Abul K. Abbas, and Jon C. Aster. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Ninth edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2015.



Kumar, Vinay, Abul K. Abbas, and Jon C. Aster. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Ninth edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2015.



Kumar, Vinay, Abul K. Abbas, and Jon C. Aster. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Ninth edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2015.
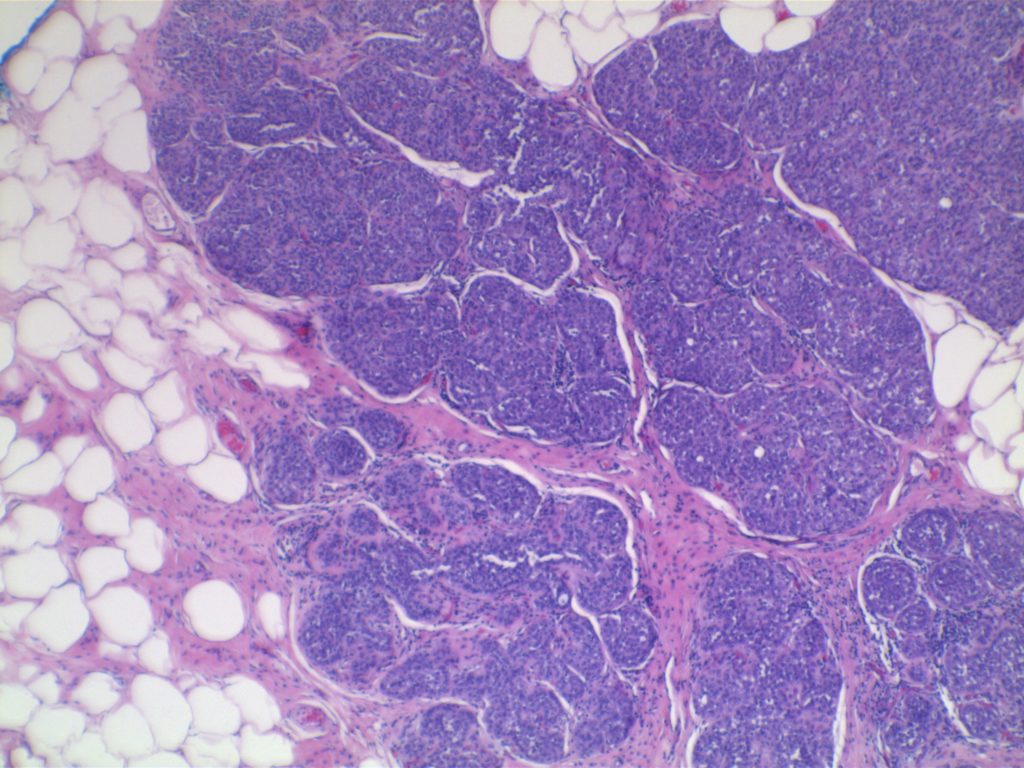
LCIS characterized by filling and expansion of the lobular unit.
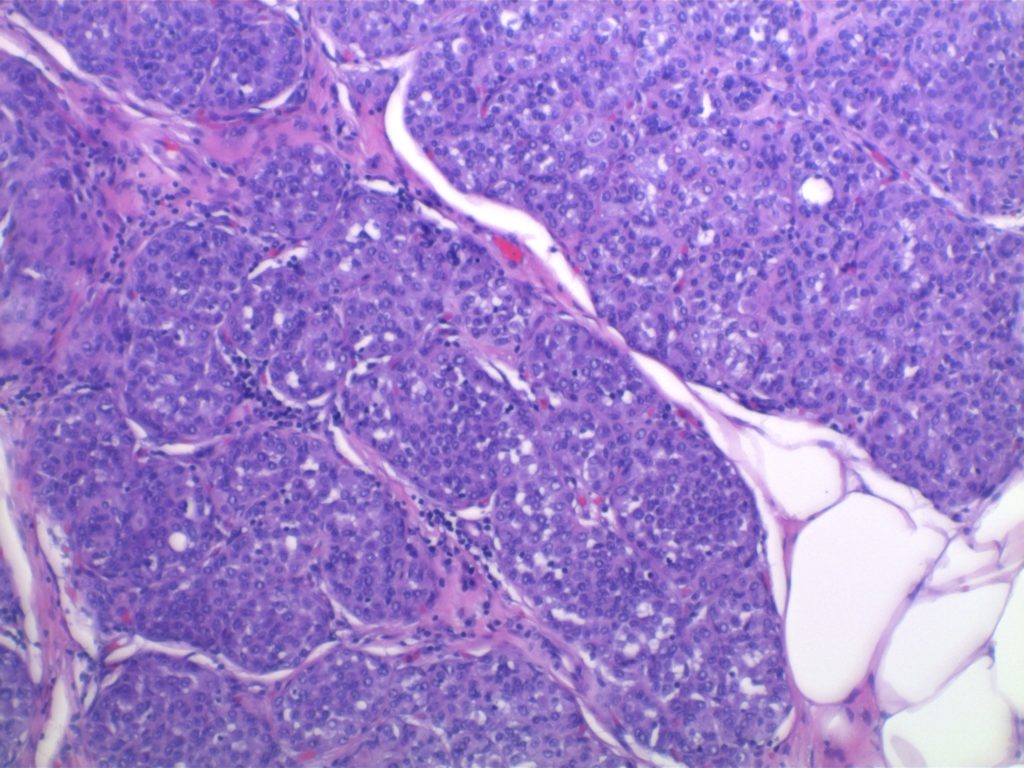
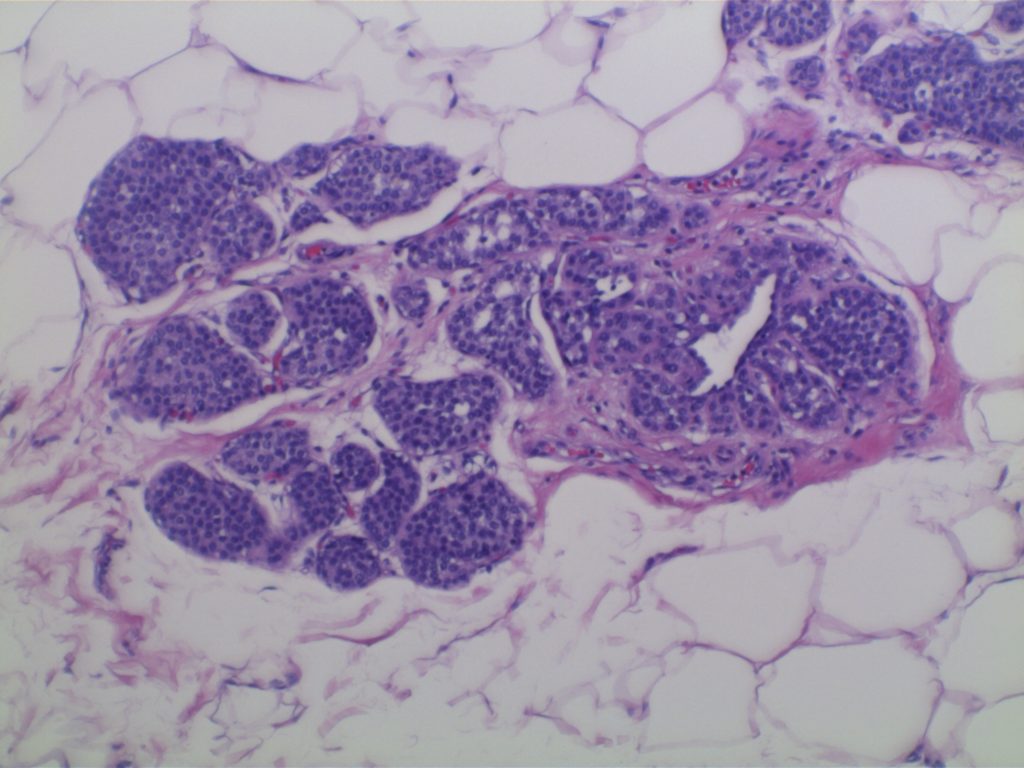
Kumar, Vinay, Abul K. Abbas, and Jon C. Aster. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Ninth edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2015. p. 1045.
|
Relative
Risk
|
Absolute
Risk
(lifetime)
|
Breast
Lesion
|
|
1
|
3%
|
|
|
1.5 – 2
|
5-7%
|
|
|
4 – 5
|
13-17%
|
|
|
8 – 10
|
25-30%
|
Kumar, Vinay, Abul K. Abbas, and Jon C. Aster. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. Ninth edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier/Saunders, 2015.
|
IHC Marker
|
Luminal Cells
|
Myoepithelial Cells
|
|
LMWCKs
(CK7/8/18)
|
Positive
|
Negative
|
|
Variable Expression
|
Negative
|
|
|
HMWCKs
(CK5/14/17)
|
Negative
|
Positive
|
|
SMA
|
Negative
|
Positive
|
|
Negative
|
Positive
|
|
|
Negative
|
Positive
|