General
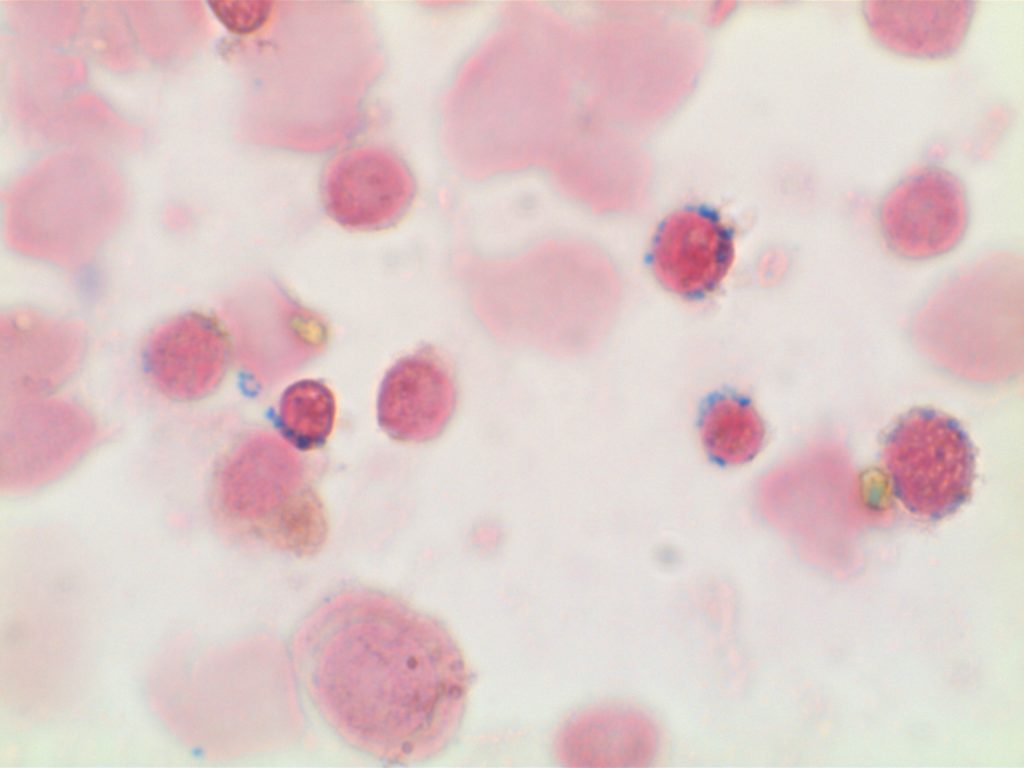
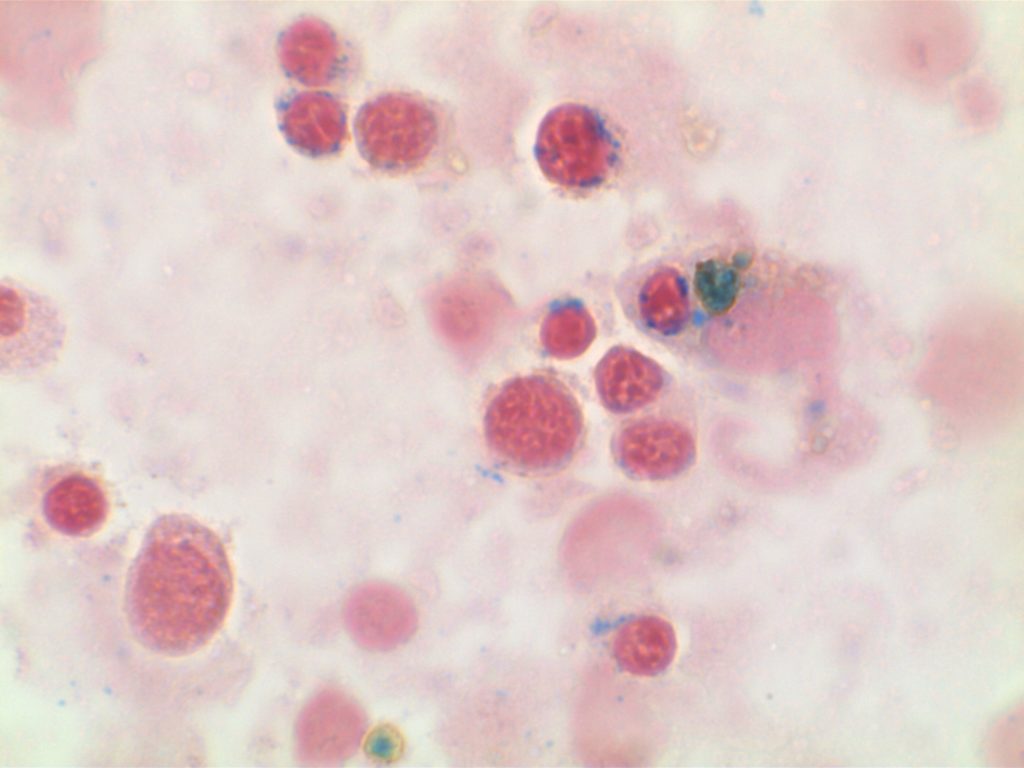
- Many cases of myelodysplasia (MDS-RS) and MDS/MPN with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN-RS-T) are associated with SF3B1 mutations.
- SF3B1 – splicosome gene, often comuted with JAK2 in cases of MDS/MPN-RS-T (less frequently CALR and MPL)
- Only 5% RS is required to diagnosis MDS-RS if a SF3B1 mutation is identified. If no mutation, then the 15% RS threshold remains.
Photomicrographs