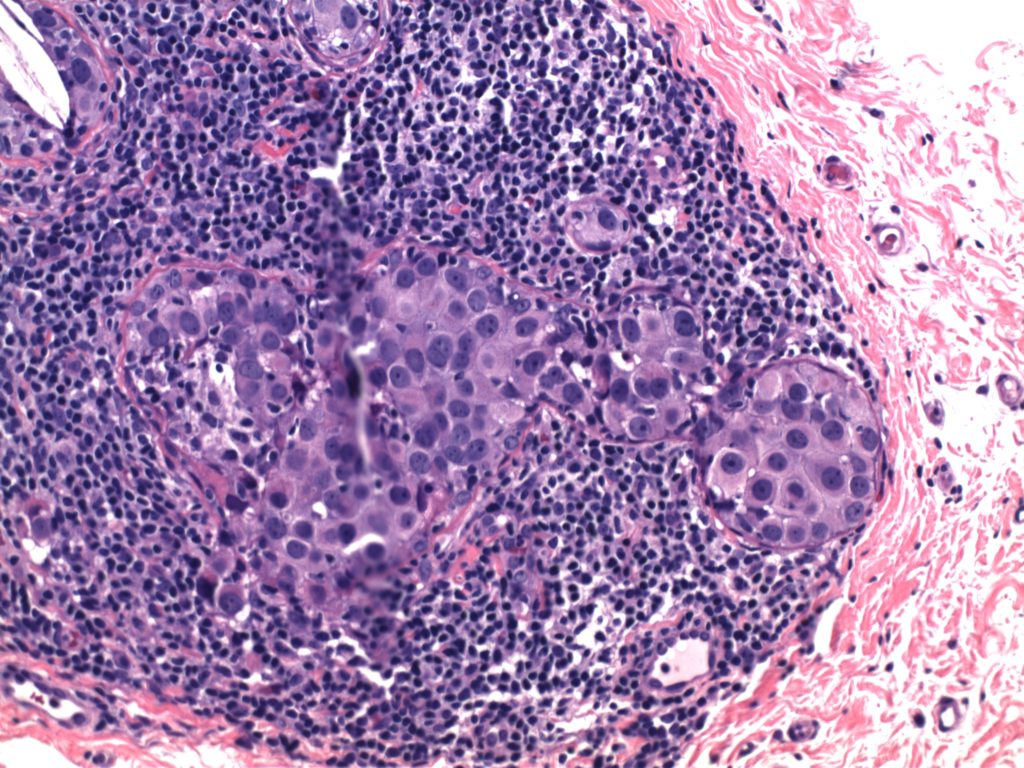
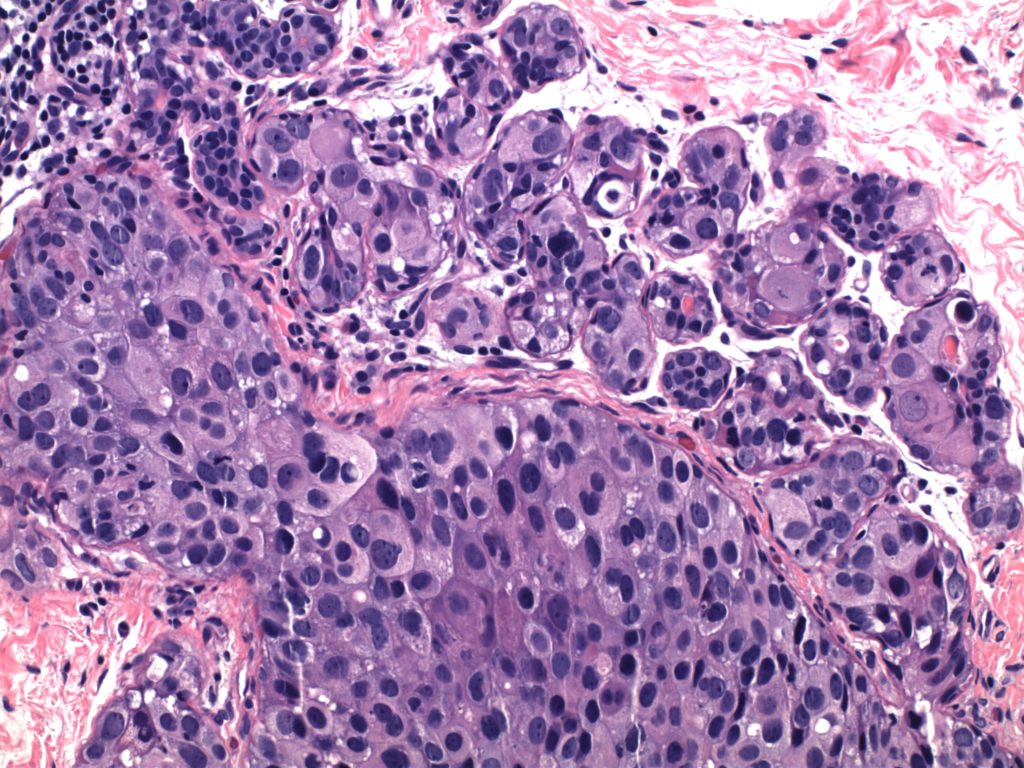
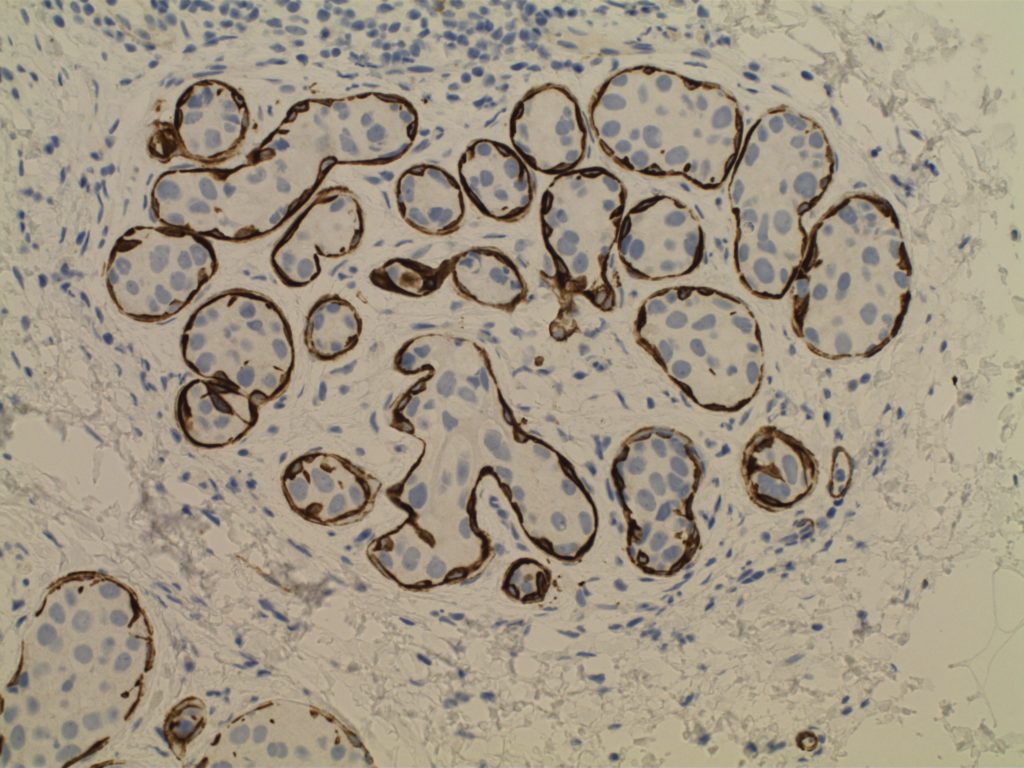
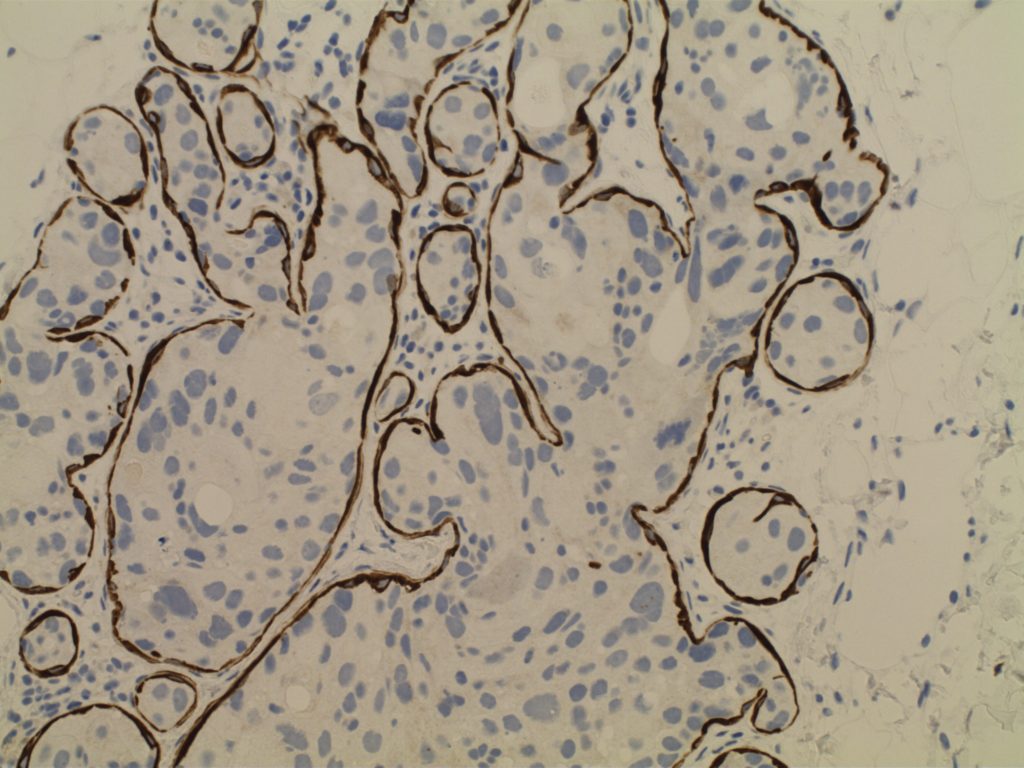
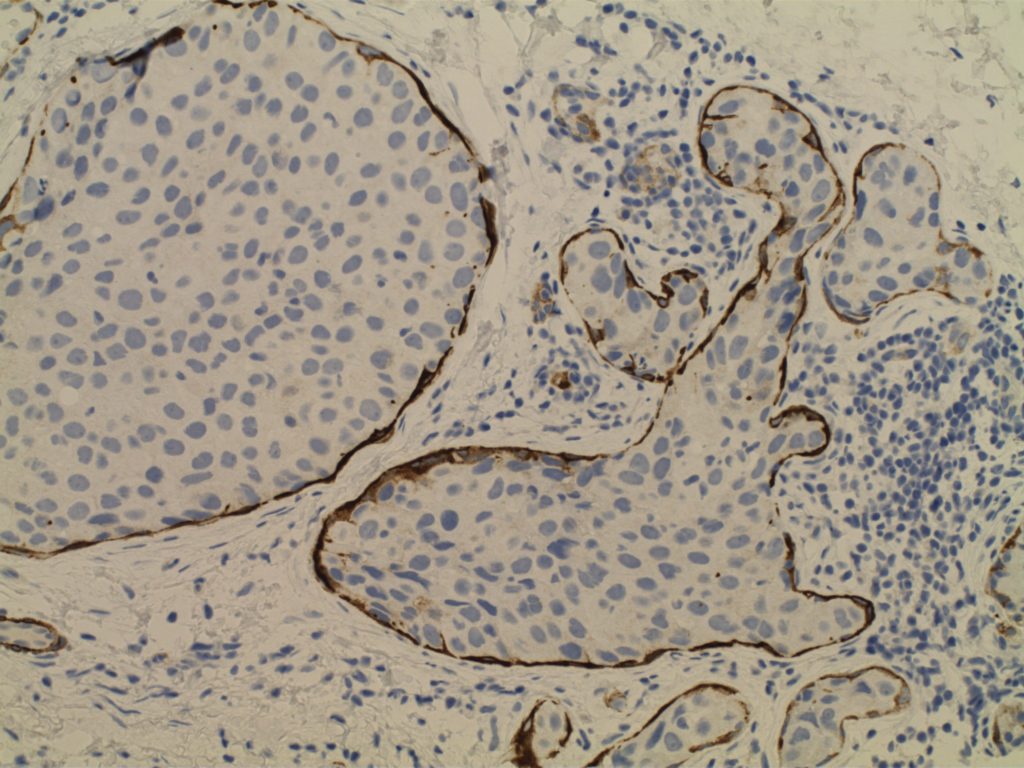
Invasive Breast Carcinoma
- Invasive breast carcinomas not segregated out as a special subtype are classified as invasive ductal carcinoma, no special type (NST). These tumors (and most of the special types) have prognosis and treatment plans based on the receptor status (and sometimes additional molecular profiling).
- Receptor testing includes ER/PR/Her-2 and Ki-67 (proliferation marker)