CD1a is a T-cell surface antigen normally expressed on cortical thymocytes (CD4+/CD8+), dendritic cells, and in activated T-cells. CD1a is a marker most commonly used in the diagnosis of Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) [CD1a+ & S-100+] and T-cell Acute Lymhpoblastic Leukemia (T-ALL). On of the most common scenarios to use CD1a is differentiating between Rosai-Dorfman Disease (S-100+/CD1a- and Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (S-100+/CD1a+).
The following highlights situations in which CD1a may be expressed or diagnostically useful.
- Benign T-cells – CD1a is not expressed in normal mature T-cells, but activated T-cells (cytoplasmic staining) may have expression (usually rare scattered positivity)
- Cortical Thymocytes – CD1a is normally expressed on CD4+CD8+ cortical thymocytes. Early T-cell precursors in the bone marrow should not express CD1a
- Thymoma – CD1a may be expressed in cases of thymoma. Does not appear to be sensitive for thymic carcinomas.
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (LCH) – LCH is characteristically defined by co-expression of CD1a and S-100. Cases of Rosai-Dorfman will be S-100 positive, but will not express CD1a.
- T-ALL – Cases of T-ALL can have variable (may be undetectable) IHC expression of CD1a. It is usually in a cytoplasmic pattern. TdT is the best marker for ALL. Interestingly the expression of CD1a appears to be relatively specific to patient age range (28-60 y/o).
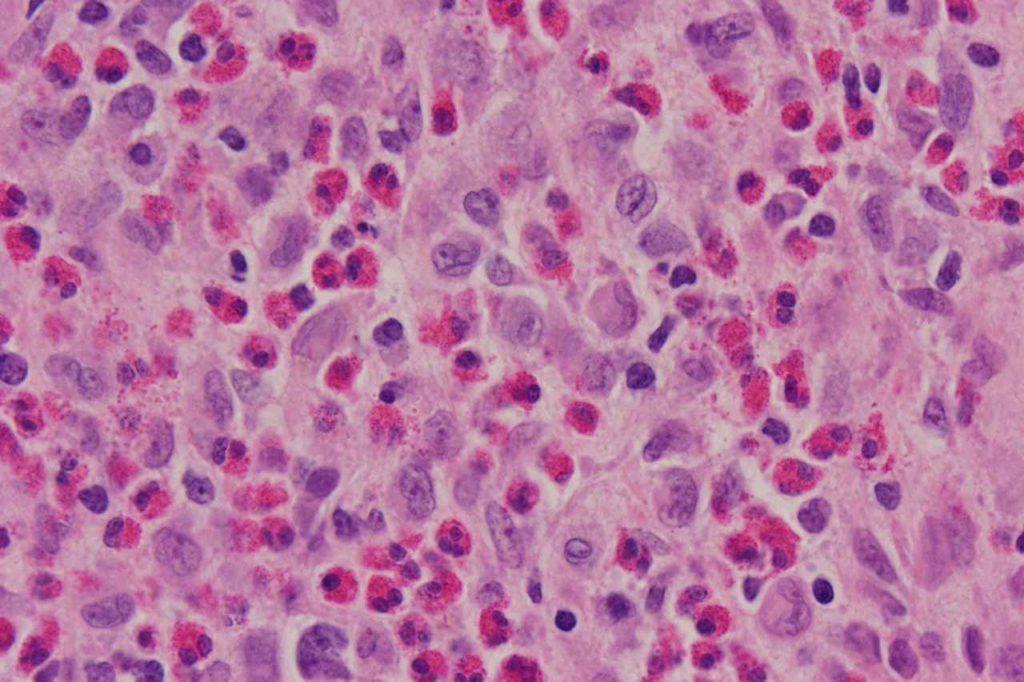
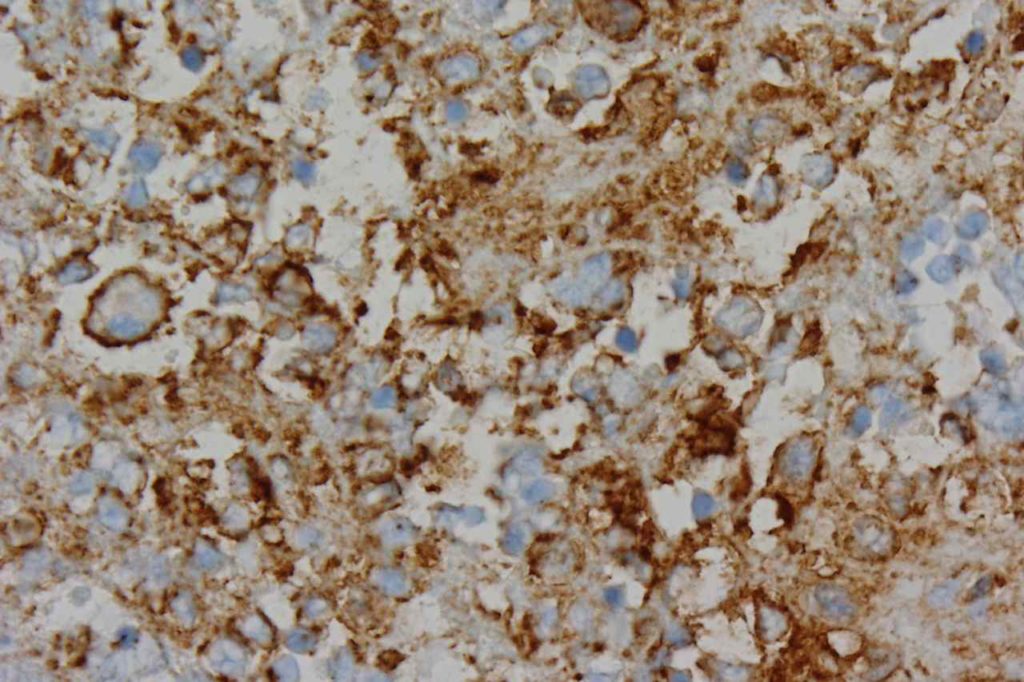
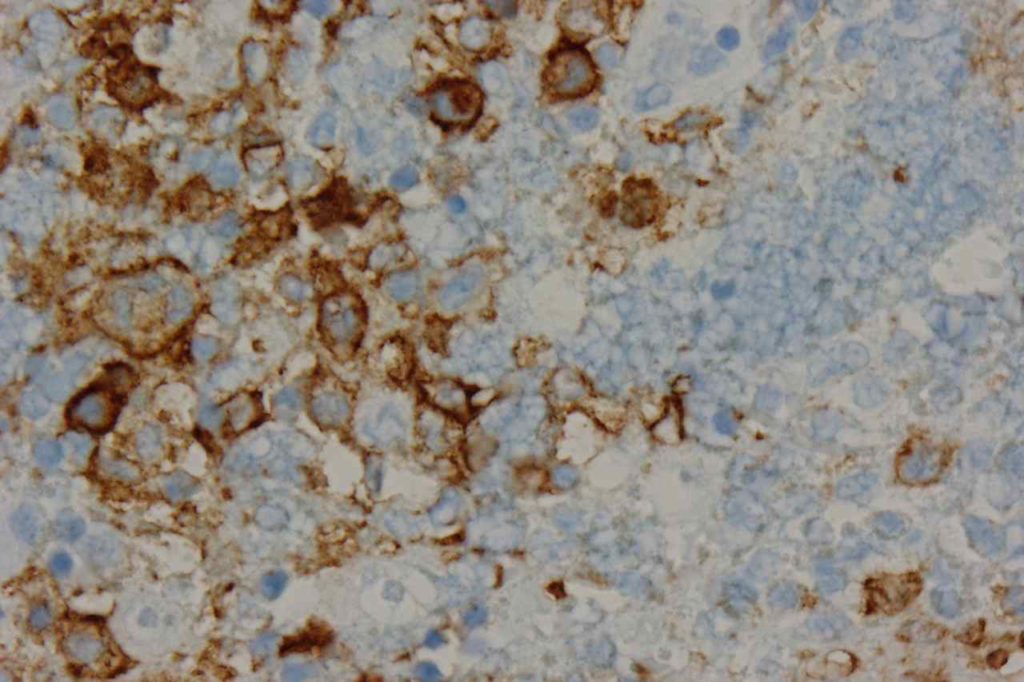
Photomicrographs
References
Bone Marrow IHC. Torlakovic, EE, et. al. American Society for Clinical Pathology Pathology Press © 2009. pp. 16-17.
Jack Longley, Jan Kraus, Miguel Alonso, and Richard Edelson. “Molecular Cloning of CD1a (T6), a Human Epidermal Dendritic Cell Marker Related to Class I MHC Molecules”. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. (1989) 92, 628–631; doi:10.1111/1523-1747.ep12712175
Onciu M, Lai R, Vega F, Bueso-Ramos C, Medeiros LJ. Precursor T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia in adults: age-related immunophenotypic, cytogenetic, and molecular subsets. Am J Clin Pathol. 2002;117: 252–258. doi:10.1309/08DJ-GPBH-H0VR-RC6F
Pomplun S, Wotherspoon AC, Shah G, Goldstraw P, Ladas G, Nicholson AG. Immunohistochemical markers in the differentiation of thymic and pulmonary neoplasms. Histopathology. 2002;40: 152–158.
O’Malley DP, Duong A, Barry TS, Chen S, Hibbard MK, Ferry JA, et al. Co-occurrence of Langerhans cell histiocytosis and Rosai-Dorfman disease: possible relationship of two histiocytic disorders in rare cases. Mod Pathol. 2010;23: 1616–1623. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.157