CD2 is a T-cell and NK cell (80-90%) marker. It also stains mast cells in mastocytosis disorders, and is variable in thymic B-cells (~50%). Some cases of AML will express CD2. CD2 does NOT stain B-cells, basophils, and mast cells in non-mastocytosis disorders. CD2 is one of the earliest T-cell markers.
Practically, CD2 is most often used as part of a T-cell panel to detect T-cell differentiation in a lymphoma of uncertain or presumed T-cell origin. CD3 is the most commonly used T-cell marker. Other T-cell markers include: CD3, CD4, CD5, CD7, and CD8. When evaluating an abnormal T-cell process it is often necessary to do a T-cell panel to look for aberrant antigen expression loss.
CD2 Expression
- T-cells (all)
- NK cells (80-90%)
- Thymic B-cells (~50%)
- Mast Cell Disorders
- AML (Subset)
Reactivity pattern: Membranous and cytoplasmic
Photomicrographs
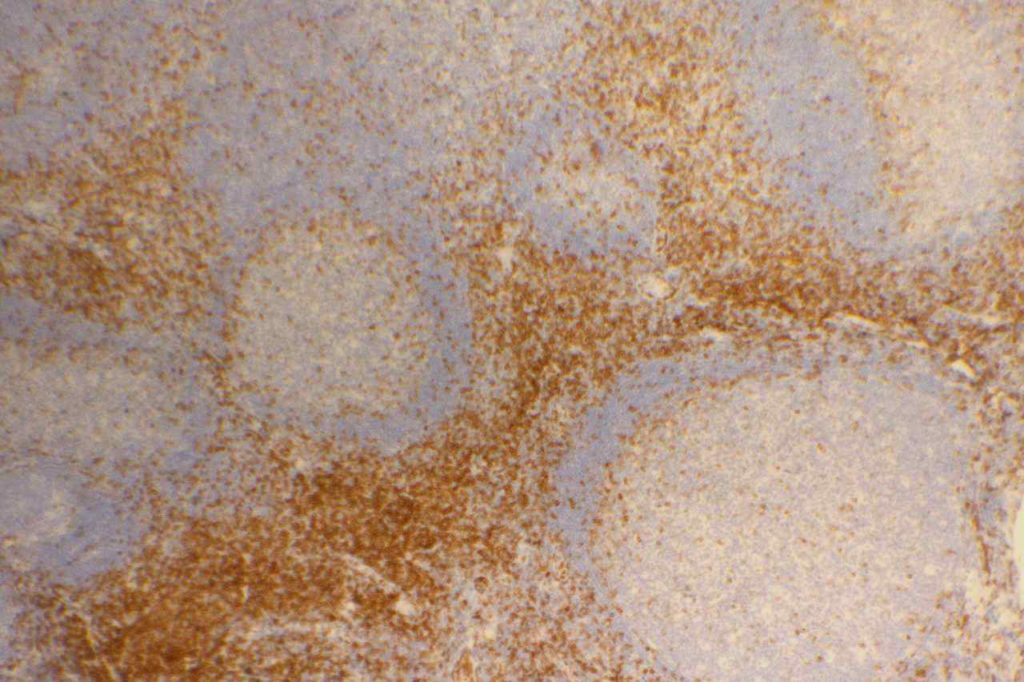
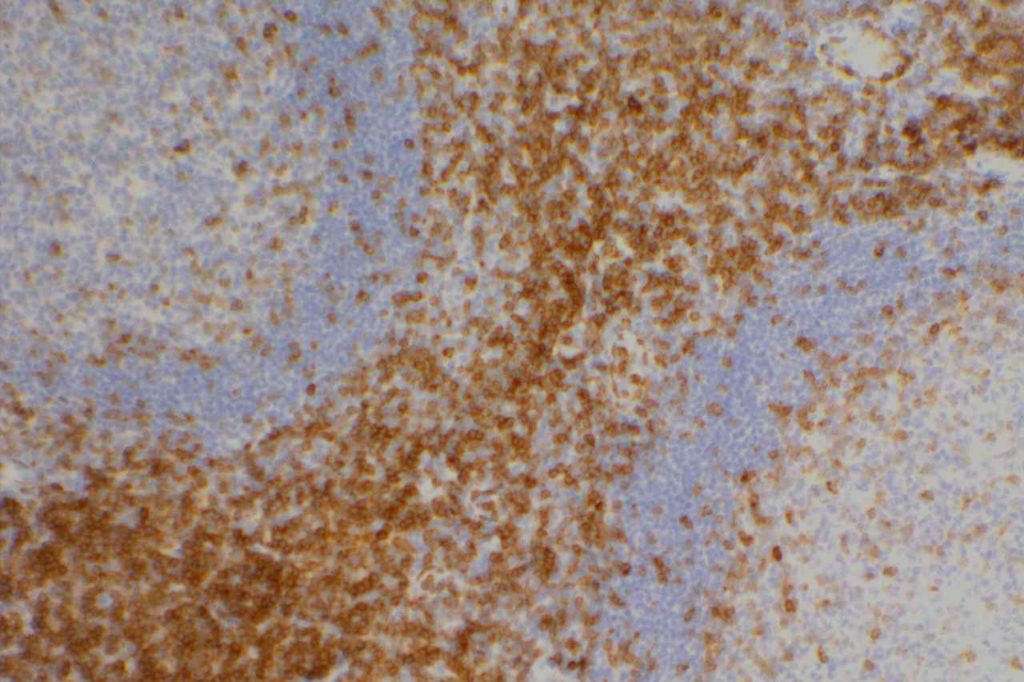
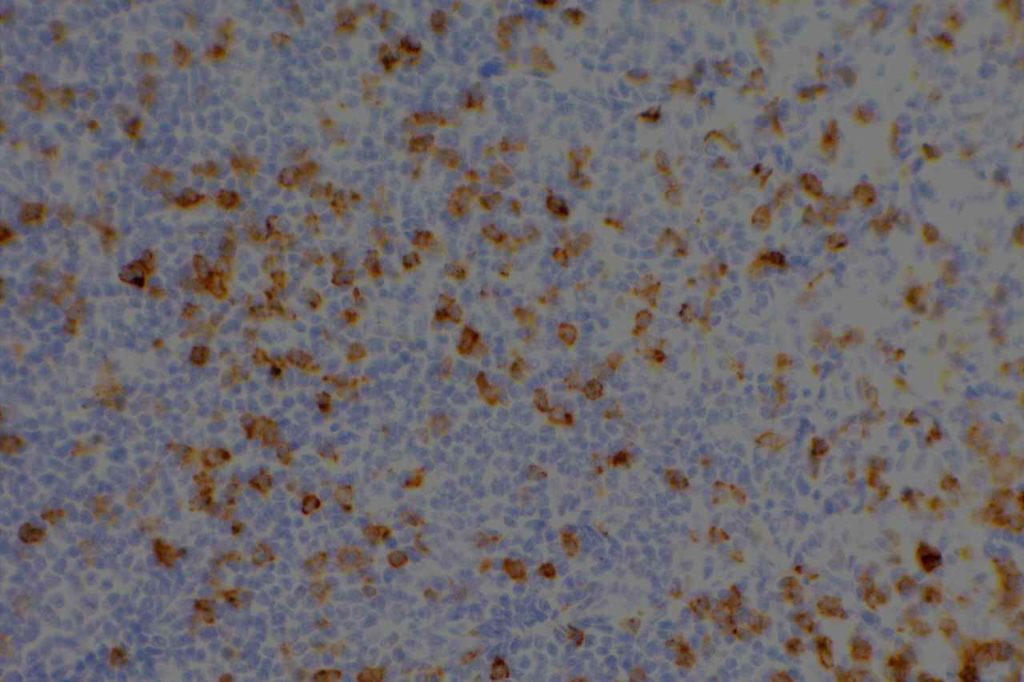
References
Bone Marrow IHC. Torlakovic, EE, et. al. American Society for Clinical Pathology Pathology Press © 2009. pp. 16-17.
Seed B, Aruffo A. Molecular cloning of the CD2 antigen, the T-cell erythrocyte receptor, by a rapid immunoselection procedure. 1987.
Davis SJ, van der Merwe PA. The structure and ligand interactions of CD2: implications for T-cell function. Immunol Today. 1996;17: 177–187.