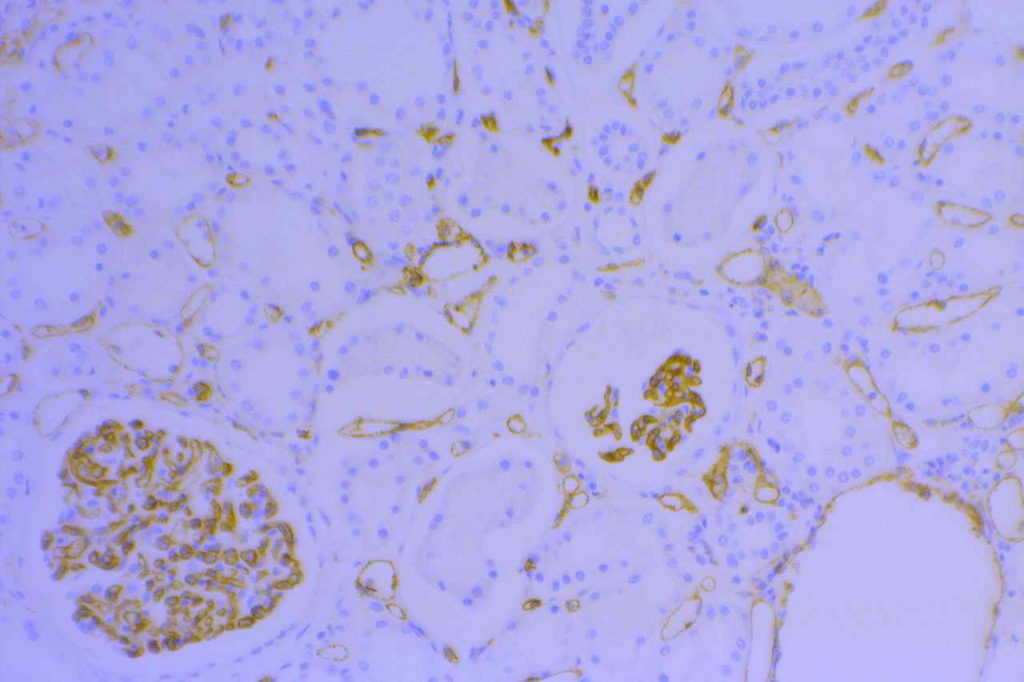
CD31 (PECAM-1) is thought of as a highly sensitive and specific marker for vascular endothelium. It is helpful to identify tumors of vascular origin, and also to identify lympho-vascular invasion by tumors. CD31 may also stain monocytes, megakaryocytic, and granulocytes in addition to endothelial cells. Plasma cells may variably express CD31 (reactive PCs more common). CD31 (like CD34) is more sensitive (and stronger staining) for blood vascular endothelium compared to lymphatic endothelium (less sensitive and variable staining).
Lymphatic & Vascular Invasion
CD31 is sometimes utilized to evaluate for “lymphovascular invasion” (LVI) in different tumors (e.g. breast more commonly). CD34 and CD31 will stain both (blood) vascular endothelium (strong & sensitive) and also lymphatic endothelium (variable & less sensitive). To determine the true nature of LVI (i.e. lymphatic vs. blood vascular invasion) additional markers specific for lymphatic endothelium (podoplanin or D2-40) need to be performed, and comparison made to CD31/CD34 for determination of invasion type:
- Lymphatic invasion – CD34/CD31 +/-, D2-40/podoplanin +
- Blood vascular invasion – CD34/CD31 +, D2-40/podoplanin –
Kaposi Sarcoma (KS)
Kaposi sarcoma is a vascular neoplasm associated with immunodeficiency (usually HIV/AIDS) and is caused by human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8). Vascular markers (CD31, CD34, D2-40, and FLI1) are helpful (in combination with HHV-8) for diagnosis. CD31 is expressed in 58-75% of cases (strong and diffuse staining). CD34 is considered more sensitive (92%).
Photomicrographs
References
Wick, MR. “Immunohistochemical approaches to the diagnosis of undifferentiated malignant tumor.”Annals of Diagnostic Pathology12(2008):72-84.
Vanchinathan V, Mirzamani N, Mizramani N, Kantipudi R, Schwartz EJ, Sundram UN. The vascular marker CD31 also highlights histiocytes and histiocyte-like cells within cutaneous tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 2015;143: 177–85– quiz 305. doi:10.1309/AJCPRHM8CZH5EMFD
Rosado FGN, Itani DM, Coffin CM, Cates JM. Utility of immunohistochemical staining with FLI1, D2-40, CD31, and CD34 in the diagnosis of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related and non-acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136: 301–304. doi:10.5858/arpa.2011-0213-OA
Morgado JMT, Sánchez-Muñoz L, Teodósio CG, Jara-Acevedo M, Álvarez-Twose I, Matito A, et al. Immunophenotyping in systemic mastocytosis diagnosis: ‘CD25 positive’ alone is more informative than the “CD25 and/or CD2” WHO criterion. Mod Pathol. 2012;25: 516–521. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2011.192
Mohammed RAA, Martin SG, Gill MS, Green AR, Paish EC, Ellis IO. Improved methods of detection of lymphovascular invasion demonstrate that it is the predominant method of vascular invasion in breast cancer and has important clinical consequences. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31: 1825–1833. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31806841f6
Bone Marrow IHC. Torlakovic, EE, et. al. American Society for Clinical Pathology Pathology Press © 2009. pp. 81.