CD7 is a T-cell marker. It is a specific T-cell marker first expressed early in T-cell development, but often one of the first to be dropped in cases of T-cell lymphoma. However, loss of CD7 expression is not SPECIFIC for lymphoma, as normal benign T-cells may also lose expression. Therefore the IHC findings must always be combined with the morphology when making a diagnosis of T-cell lymphoma. CD7 is typically used as part of a larger T-cell panel including CD2, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD7, and CD8. In challenging cases TCR gene rearrangement studies may also be helpful (specificity is not as good as B-cell gene rearrangement studies).
Aberrant expression of CD7 (and other T- and B-Cell markers) may be seen in acute leukemias (sometimes a helpful finding as a strategy for detecting minimal residual disease by flow cytometry).
CD7 Expression
- Thymocytes
- Mature T-cells
- T-ALL
- Mycosis Fungoides (often drops CD7 expression)
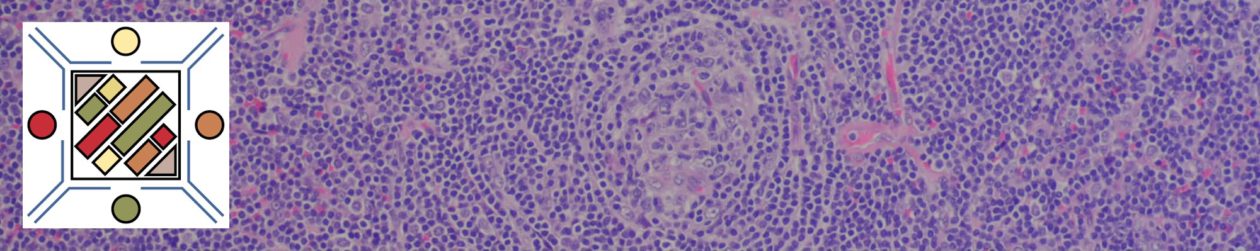
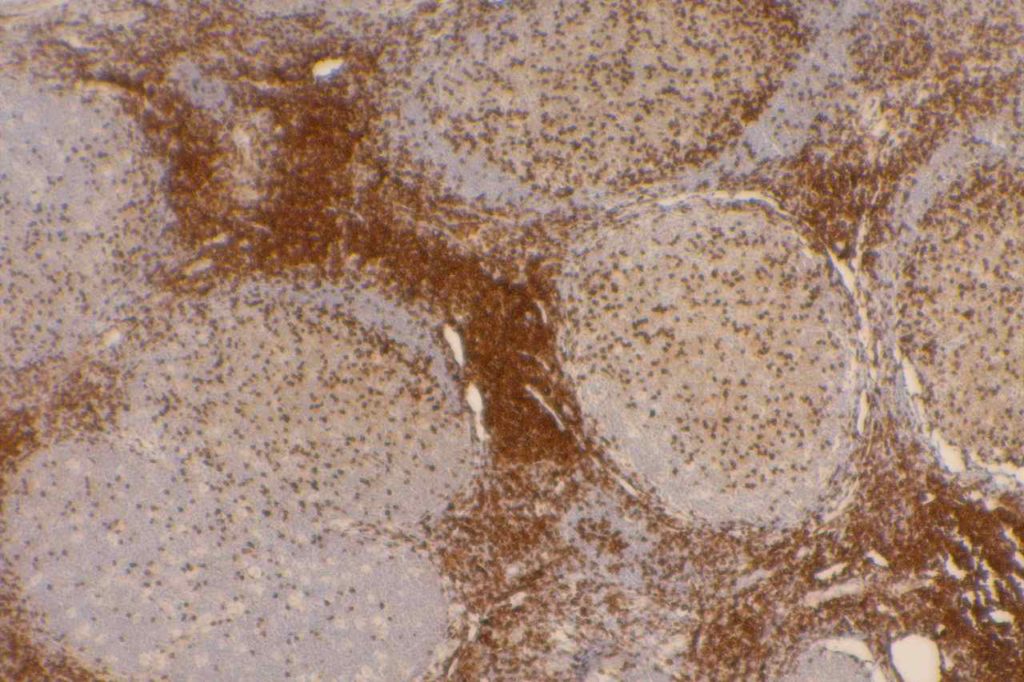
Photomicrographs
References
Bone Marrow IHC. Torlakovic, EE, et. al. American Society for Clinical Pathology Pathology Press © 2009. pp. 31-32.
Campbell SM, Peters SB, Zirwas MJ, Wong HK. Immunophenotypic diagnosis of primary cutaneous lymphomas: a review for the practicing dermatologist. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3: 21–25.
Jaffe ES, Nicolae A, Pittaluga S. Peripheral T-cell and NK-cell lymphomas in the WHO classification: pearls and pitfalls. Mod Pathol. 2013;26 Suppl 1: S71–87. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2012.181