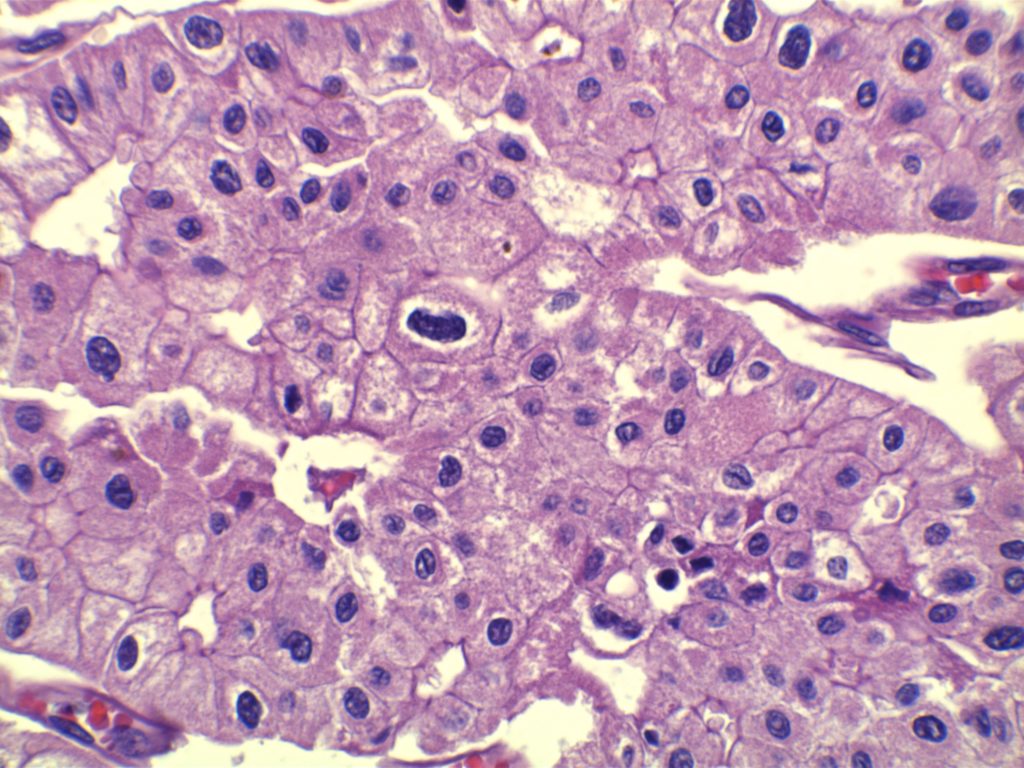
Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma is not uncommon subtype characterized by pale eosinophilic cytoplasm, rigid cell membranes (vegetable cell-like), and perinuclear halos. These cases constitute approximately 5% of renal cell cancers. These tumors are thought to arise from the intercalated cells of the collecting ducts, and have a relatively good prognosis compared to conventional renal cell carcinomas. Many experts believe that chromophobe renal cell carcinoma and oncocytoma represented to ends of the spectrum. Interestingly, oncocytomas share some molecular abnormalities with chromophobe renal cell carcinomas.
Immunohistochemistry
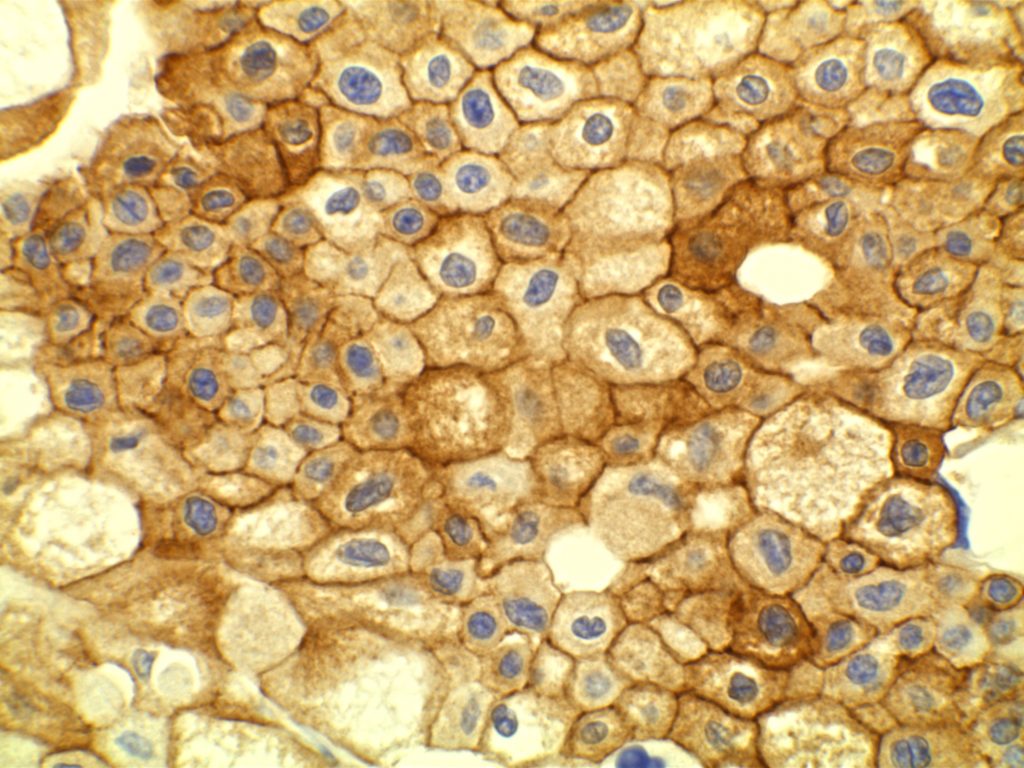
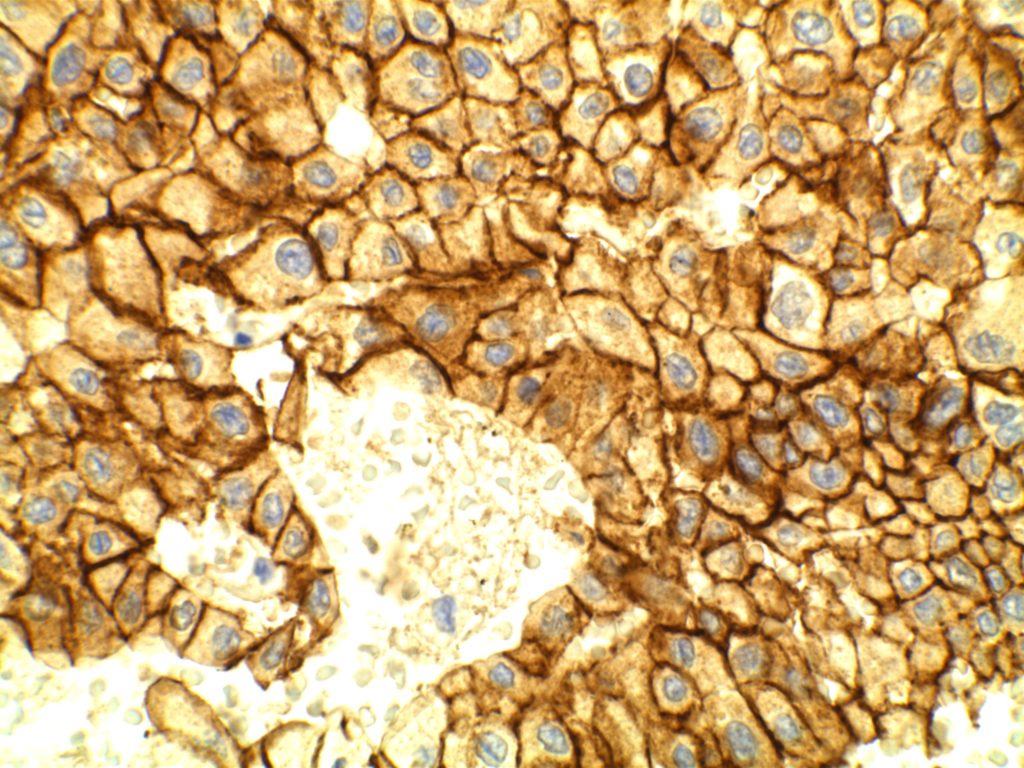
- CK7 – Positive
- CD117 – Positive
- AE1/AE3 – Positive
- Vimentin – Negative
- AMACR – Negative
- Colloidal Iron – Positive
Photomicrographs
References
Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. V Kumar, et al. 9th Edition. Elsevier Saunders. 2015.
Truong LD, Shen SS. Immunohistochemical diagnosis of renal neoplasms. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;135: 92–109. Available: http://www.archivesofpathology.org/doi/pdf/10.1043/2010-0478-RAR.1