General
Ki-67 is a proliferation marker with nuclear staining. It is expressed in cells in G1, S, G2 and M phases of the cell cycle. This marker is used in many ways, and often carries prognostic information for many malignancies (breast, certain lymphomas, etc.). It is also used as a diagnostic aid in certain difficult cases (e.g. cervical dysplasia, melanocytic tumors, etc.).
When using this stain diagnostically, one should understand the clinical significance for the diagnostic circumstance in which the stain is being used, and have appropriate knowledge of the medical literature with respect to the staining performance in the given clinical-pathologic setting. For example low grade lymphomas would be expected to have a relatively low-proliferation staining index (<30%), whereas Burkitt Lymphoma would have a high staining index (>95%).
Clone: MIB-1 (most common)
Photomicrographs
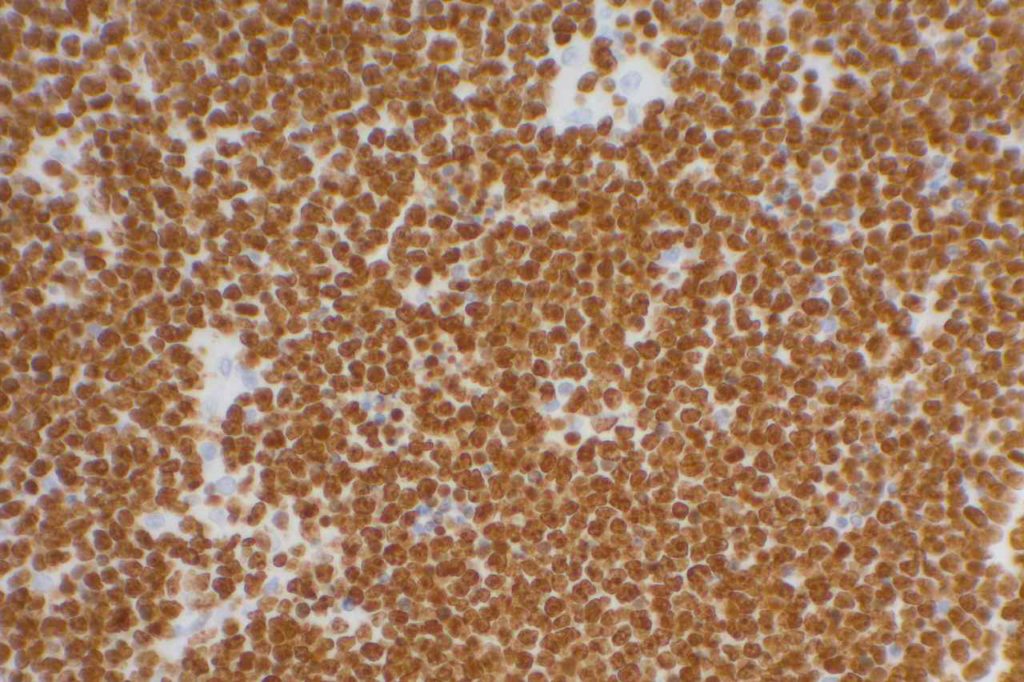
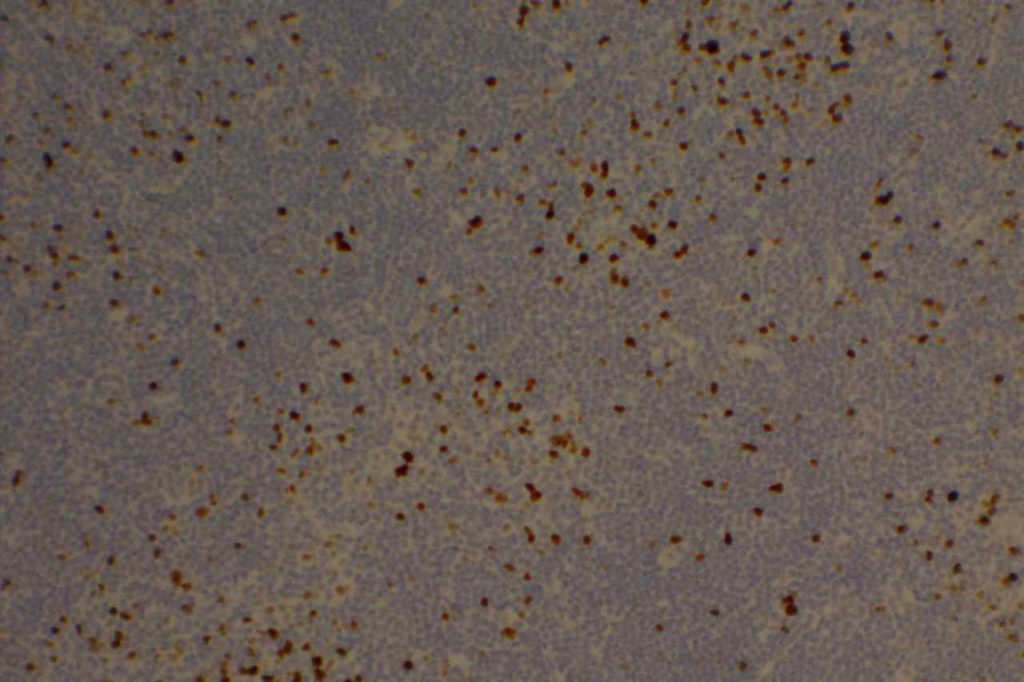
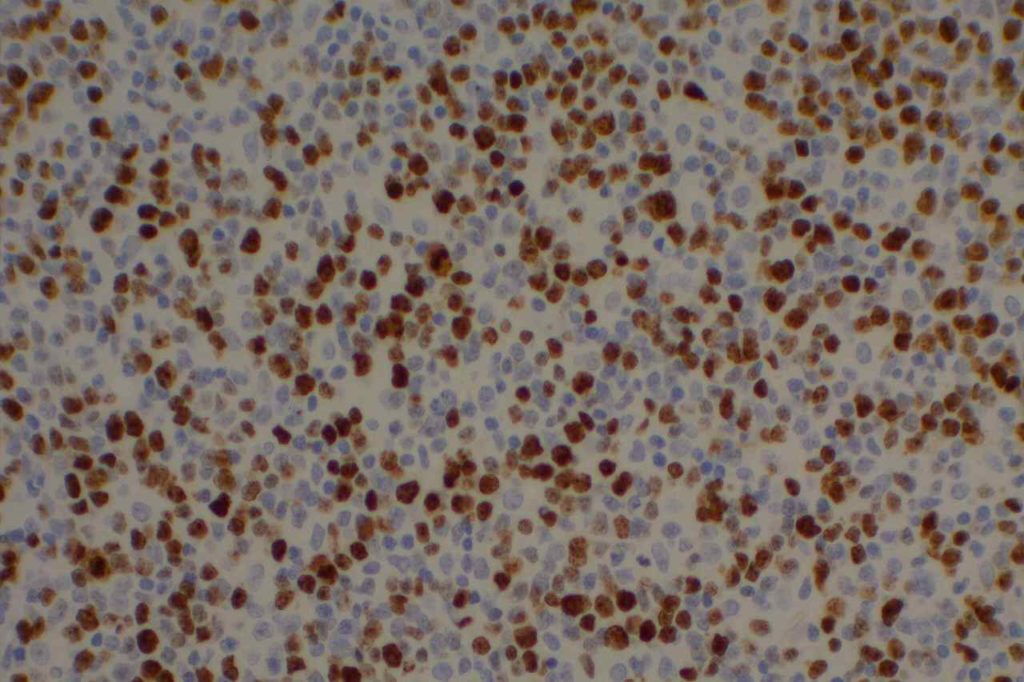
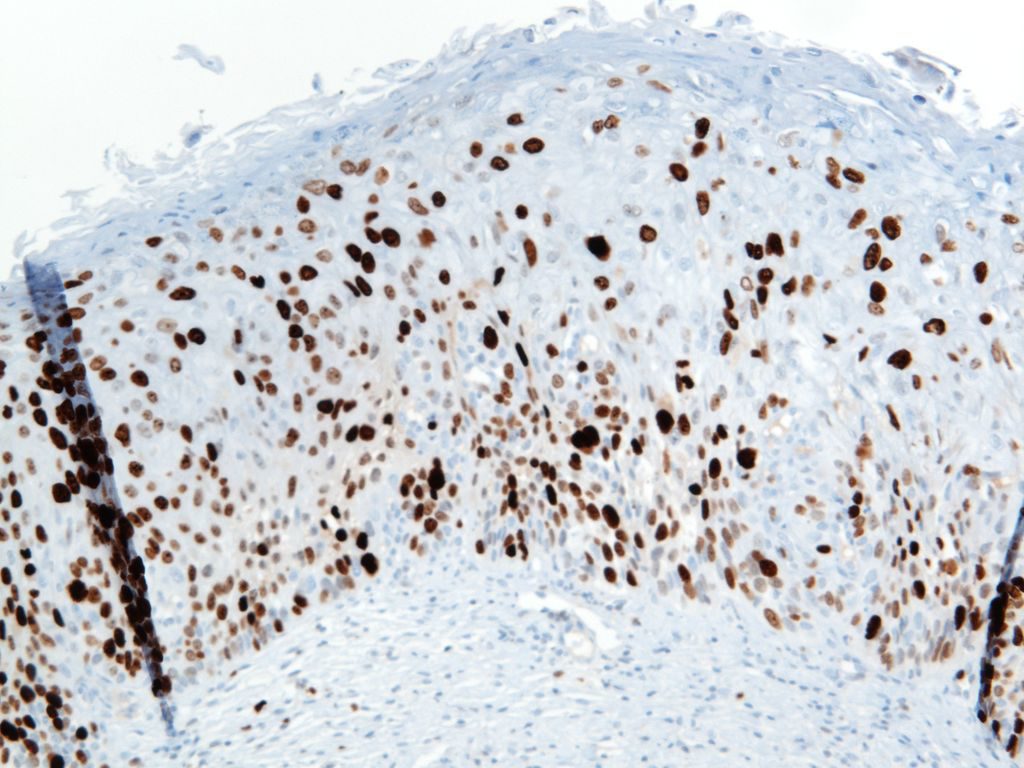
Reference:
Katzenberger, T., Petzoldt, C., Höller, S., Mäder, U., Kalla, J., Adam, P., et al. (2006). The Ki67 proliferation index is a quantitative indicator of clinical risk in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood, 107(8), 3407. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-10-4079
McCall, C. M., Shi, C., Cornish, T. C., Klimstra, D. S., Tang, L. H., Basturk, O., et al. (2013). Grading of well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors is improved by the inclusion of both Ki67 proliferative index and mitotic rate. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 37(11), 1671–1677. doi:10.1097/PAS.0000000000000089
Bone Marrow IHC. Torlakovic, EE, et. al. American Society for Clinical Pathology Pathology Press © 2009. pp. 209.