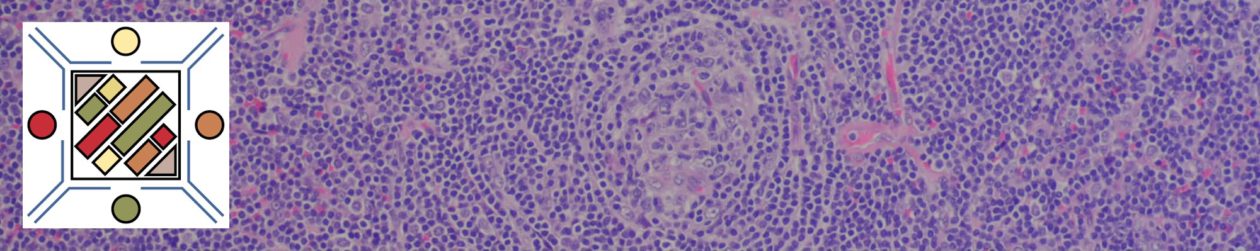
This is a special subtype of B-cell lymphoma, which may have an entirely diffuse, diffuse and follicular, or exclusive follicular pattern. It is typically characterized by strong IRF4/MUM-1 expression by immunohistochemistry. An IRF4 rearrangement is typically found. This lymphoma most commonly occurs in children or young adults in the head and neck region (especially Waldeyer ring).
Morphologically these cases would otherwise be characterized as a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma, or combined follicular and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In the pure follicular pattern, some have referred to this as “Waldeyer Ring Follicular Lymphoma.” Suspicion should be raised based on the patient’s age, disease location, and coexpression of CD10 and MUM-1.
Immunophenotype
- CD20 positive
- CD79a positive
- PAX-5 positive
- MUM-1 strongly expressed
- BCL-6 positive
- PRDM1 (BLIMP1) typically negative
- CD10 usually positive (66%)
- BCL-2 usually positive (66%)
- Ki-67 high (lack of evidence of polarization in neoplastic follicles)
Cases with a phenotype of CD10 coexpression with MUM-1 should be considered for IRF4 rearrangements screening. The prognosis is relatively good with appropriate treatment.
References
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris, NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J (Eds): WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues (Revised 4th edition). IARC: Lyon 2017
Fedoriw Y, Dogan A. The Expanding Spectrum of Follicular Lymphoma. Surg Pathol Clin. 2016;9: 29–40. doi:10.1016/j.path.2015.11.001
Salaverria I, Philipp C, Oschlies I, Kohler CW, Kreuz M, Szczepanowski M, et al. Translocations activating IRF4 identify a subtype of germinal center-derived B-cell lymphoma affecting predominantly children and young adults. Blood. 2011;118: 139–147. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-01-330795