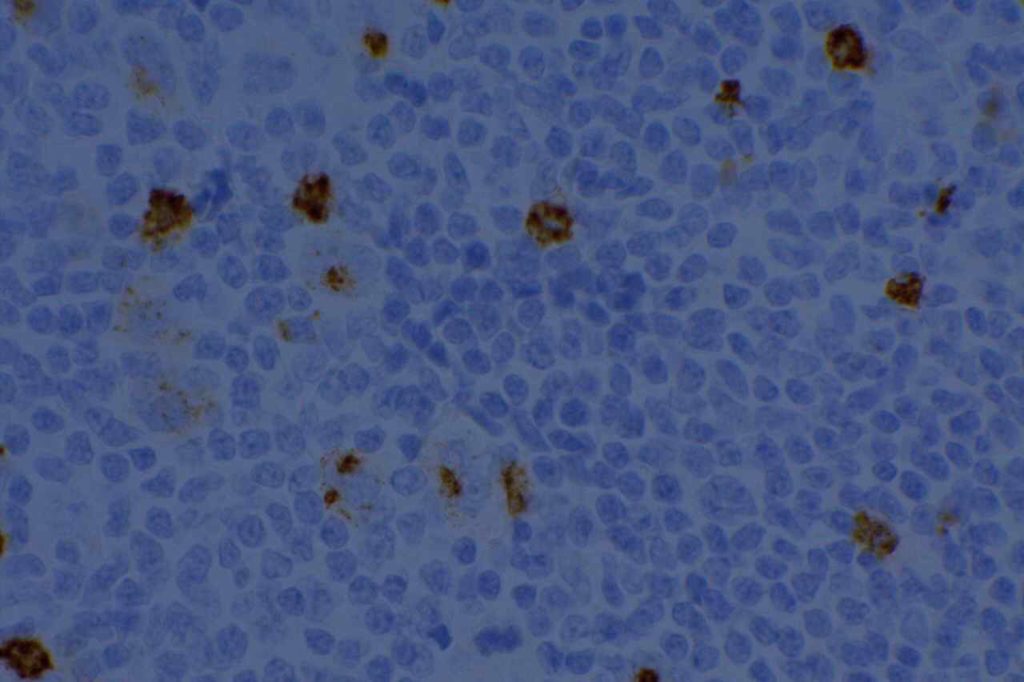
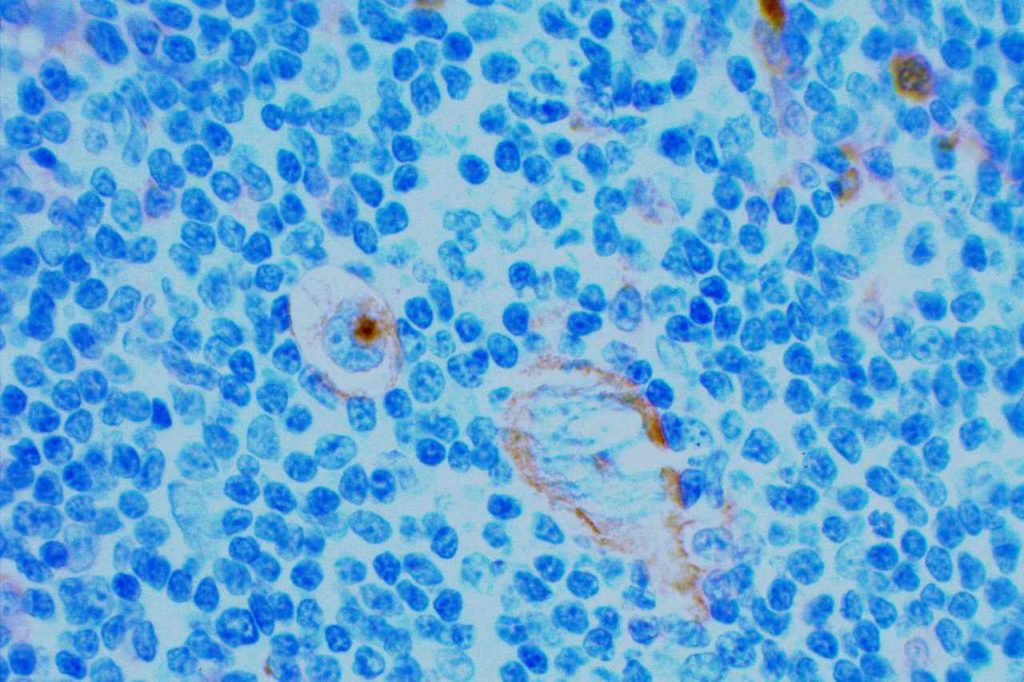
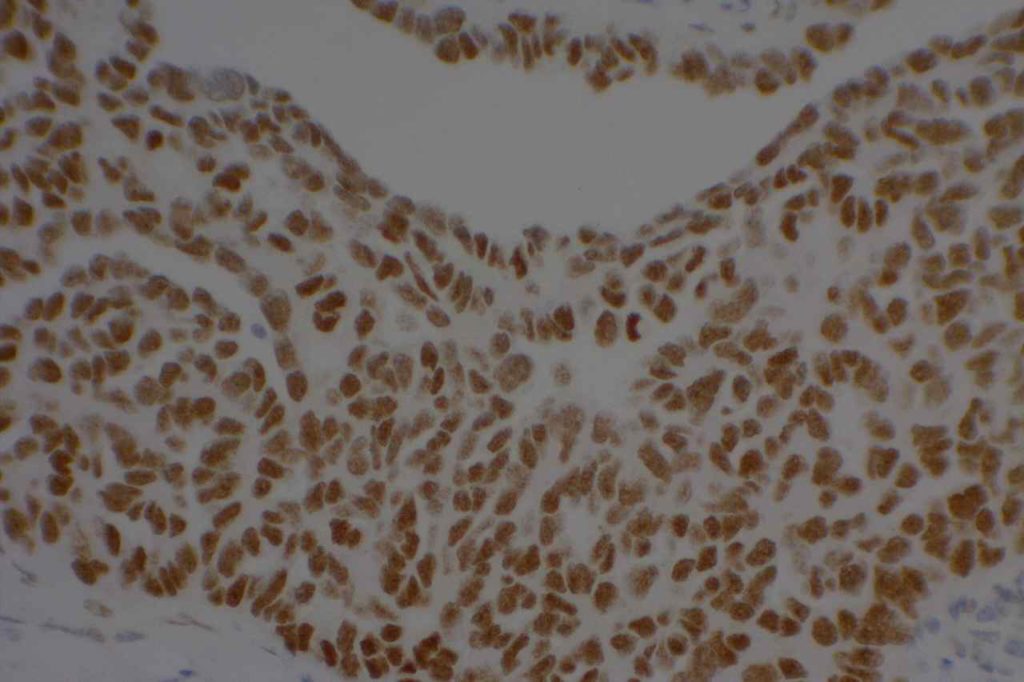
WT-1 (Wilms tumor gene product) is a marker most commonly used to identify OVARIAN SEROUS CARCINOMAS. It is also commonly used in a panel to differentiate mesothelioma (positive) from adenocarcinoma (negative). WT-1 has a normal expression distribution in adult tissues, which includes Sertoli cells, ovarian stromal and surface epithelium, and mesothelium. The 6F-H2 clone has shown better sensitivity compared to other WT-1 antibodies (Ordonez).
Tumors / lesions expressing WT-1:
- Mesothelioma (>75% of epithelial mesotheliomas, usually negative in sarcomatoid variants)
- Ovarian Serous Carcinomas
- Wilms tumor
- Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumors
- Metanephric Adenomas
|
Tumor
|
Expression (%)
|
|
Ovarian Serous Carcinoma
|
93%
|
|
Ovarian Mucinous Carcinoma
|
0%
|
|
Pancreatobiliary Carcinoma
|
0%
|
|
Breast Carcinoma
|
0%
|
|
Lung Carcinoma
|
0%
|
|
Colon Adenocarcinoma
|
0%
|
|
Renal Cell Carcinoma
|
0%
|
|
Thyroid Carcinoma
|
0%
|
|
Prostate Adenocarcinoma
|
0%
|
WT-1 expression in differentiating mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma (Marchevsky).
|
Tumor
|
Expression (%)
|
|
Epithelioid Mesothelioma
|
77%
|
|
Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
|
13%
|
|
Adenocarcnioma
|
4%
|
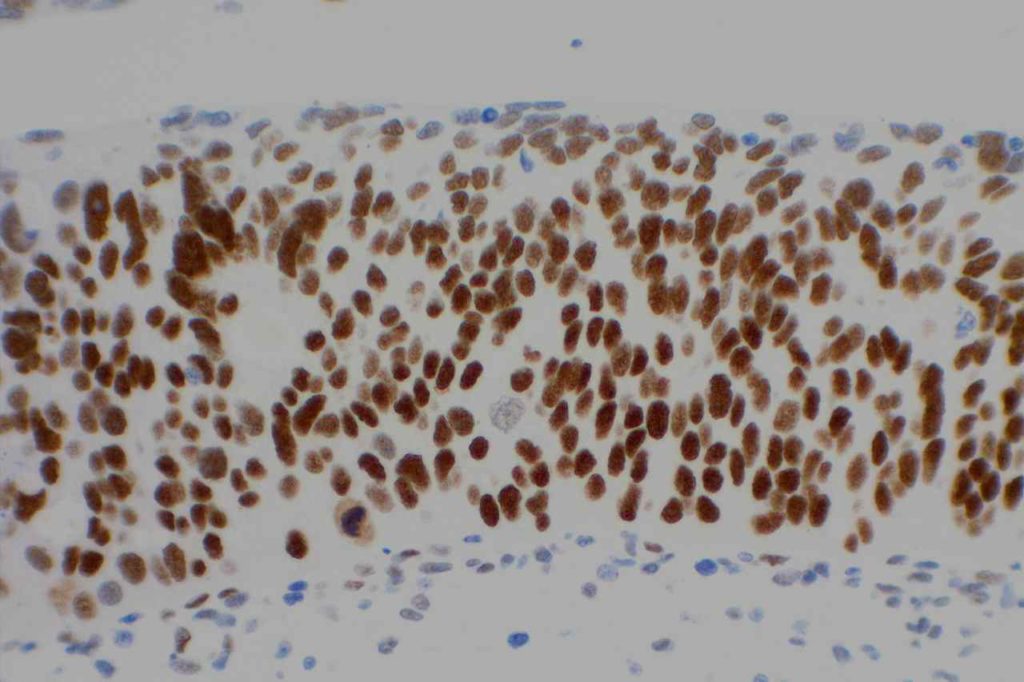
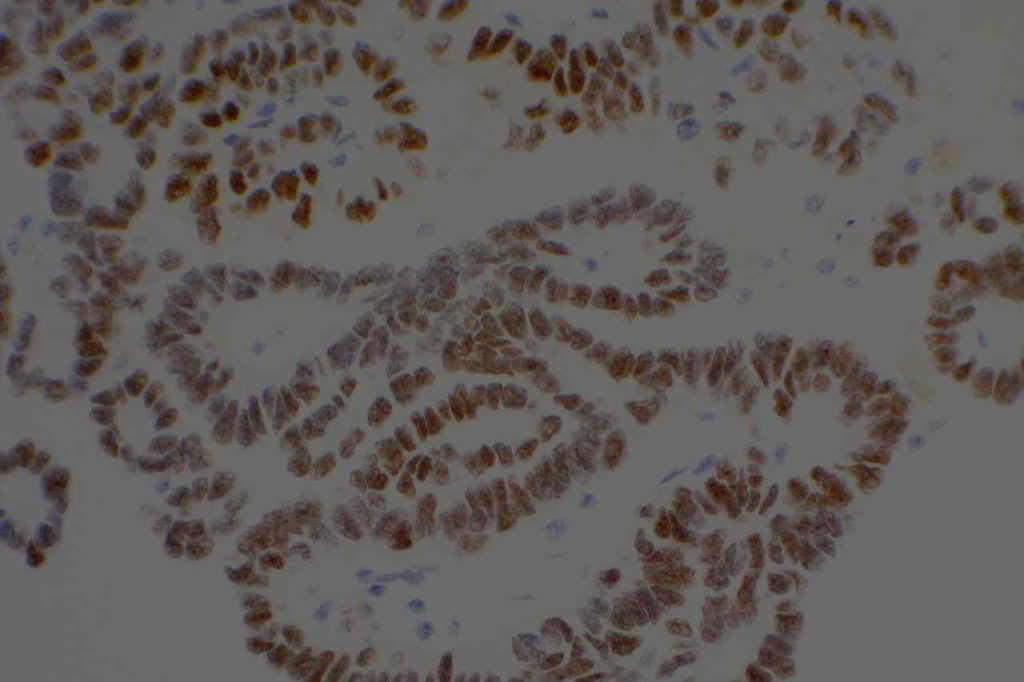
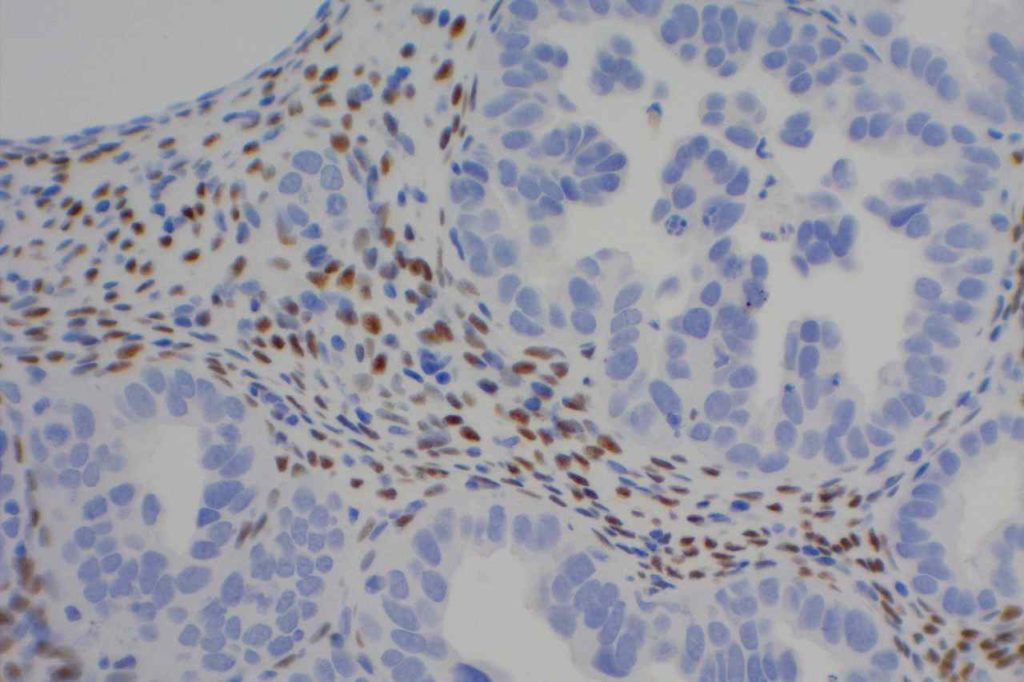
Photomicrographs
References:
Muir, T. E., Cheville, J. C., & Lager, D. J. (2001). Metanephric adenoma, nephrogenic rests, and Wilms’ tumor: a histologic and immunophenotypic comparison. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 25(10), 1290–1296.
Marchevsky, A. M. (2008). Application of immunohistochemistry to the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma. Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine, 132(3), 397–401.
Ordóñez, N. G. (2005). Immunohistochemical diagnosis of epithelioid mesothelioma: an update. Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine, 129(11), 1407–1414.
Hadi, AIMM Annual Meeting, “Carcinomas of Unknown Primary”, presentation, 2011.