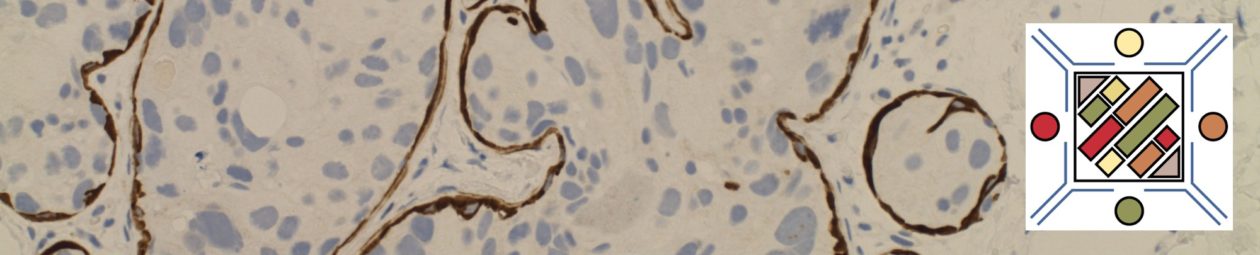
A common differential diagnosis in breast lesions is between usual type hyperplasia (UDH) and atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH)/ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). In difficult cases there are some immunohistochemical patterns, which may be helpful to differentiate between diagnoses. UDH has mosaic expression pattern with HMWK (high molecular weight keratins) (e.g. CK5 or CK5/6) whereas ADH/DCIS typically does not. ADH/DCIS does typically has strong uniform up regulation of estrogen receptor (ER) in contrast to UDH.
DIAGNOSTIC FEATURES
Cellular Population
|
Florid UDH
|
ADH
|
|
True hyperplasia contains a mixture of cell types (streaming, slit-like spaces)
|
Clonal population of monotonous cells with rigid “punched-out” spaces
|
CK Expression
|
Florid UDH
|
ADH
|
|
Mixture of basal cells (CK5/14/17) and luminal cells (CK7/8/18)
|
Monotonous population of luminal cell types (CK 7/8/18)
|
ER Expression
|
Florid UDH
|
ADH
|
|
Variable patchy expression
|
Usually uniform strong expression
|
Breast Cancer Relative Risk
|
Florid UDH
|
ADH
|
|
Slightly increased (1.5-2 X)
|
Moderately increased (3.7-5.3 X)
|
|
Diagnostic Features
|
Florid UDH
|
ADH
|
|
Cellular Population
|
True hyperplasia contains a mixture of cell types (streaming, slit-like spaces)
|
Clonal population of monotonous cells with rigid “punched-out” spaces
|
|
CK Expression
|
Mixture of basal cells (CK5/14/17) and luminal cells (CK7/8/18)
|
Monotonous population of luminal cell types (CK 7/8/18)
|
|
EP Expression
|
Variable patchy expression
|
Usually uniform strong expression
|
|
Breast Cancer R.R.
|
Slightly increased (1.5-2X)
|
Moderately increased (3.7-5.3X)
|
References
Hicks DG. Immunohistochemistry in the diagnostic evaluation of breast lesions. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2011;19(6):501–505. doi:10.1097/PAI.0b013e31822c8a48.
Liu H. Application of immunohistochemistry in breast pathology: a review and update. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138(12):1629–1642. doi:10.5858/arpa.2014-0094-RA.